Table of Contents
Cell Wall Structure and Function
In this article we will discuss about:- What is cell wall?, Characteristics of Cell Wall, Cell Wall Structure, What is Pits and its types and Functions of cell wall
What is Cell Wall?
- Cell wall is rigid and protective layer around the plasma membrane
- Discovered by Robert hooke in 1665
- Cell wall non-living rigid structure
- Found in plants, fungi, prokaryotes and protists
- Composition of cell wall varies in different groups
Characteristics of Cell Wall
- Cell wall is a rigid and protective layer around the plasma membrane
- It is a non-living structure
- Animal cells do not have a cell wall
- Found in in most plant cells, fungi, bacteria, algae, and some archaea
- Cell wall has many important functions in a cell including protection, structure, and support
Cell Wall Structure
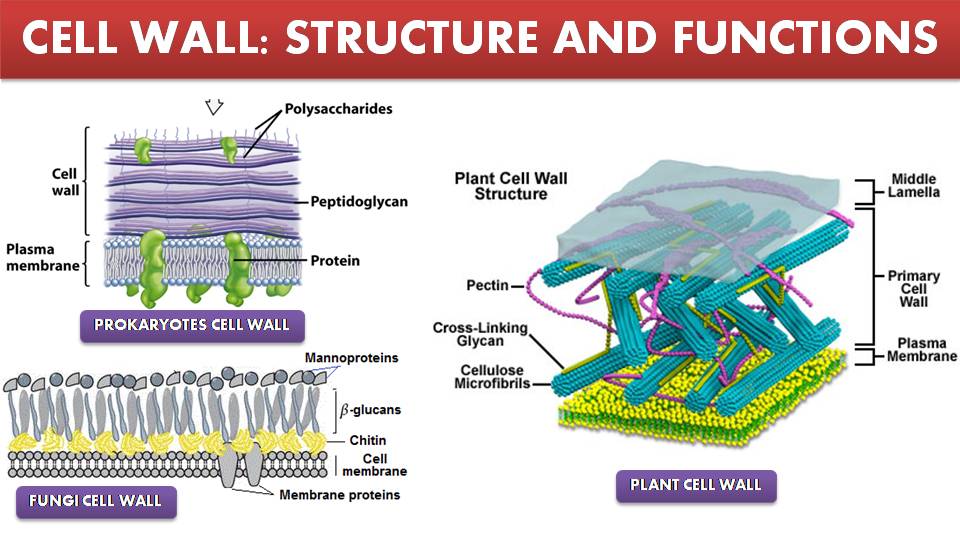
Structure of Prokaryotes Cell Wall
- Cell wall is made up of peptidoglycon
- peptidoglycan made up of polysaccharide chains cross-linked by unusual peptides containing D-amino acids
- A notable difference between the cell walls of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria is the substantially thicker peptidoglycan layer in gram-positive bacteria.
- Cell wall of gram-positive bacteria contains teichoic acids
Structure of Fungi Cell Wall
- Fungal cell wall is made up of three main components
Chitin
- Polymers consisting mainly of unbranched chains of β-(1,4)-linked-N-Acetylglucosamine in the Ascomycota and Basidiomycota, or poly-β-(1,4)-linked-N-Acetylglucosamine (chitosan) in the Zygomycota
- Both chitin and chitosan are synthesized and extruded at the plasma membrane
Glucans
- Glucose polymers that function to cross-link chitin or chitosan polymers
- β-glucans are glucose molecules linked via β-(1,3)- or β-(1,6)- bonds and provide rigidity to the cell wall while α-glucans are defined by α-(1,3)- and/or α-(1,4) bonds and function as part of the matrix
Proteins
- Enzymes necessary for cell wall synthesis and lysis in addition to structural proteins are all present in the cell wall.
- Most of the structural proteins found in the cell wall are glycosylated and contain mannose, thus these proteins are called mannoproteins or mannans.
Structure of Plant cell wall
- Cell wall is made up of 4 layers
- Middle lamella, primary, secondary and tertiary wall
I) Middle lamella
- Cementing layer between the cells
- It is made up of ca & mg pectates
II) Primary cell wall
- Found in growing cell
- It has high hemicelluloses & less cellulose content
III) Secondary cell wall
- Found in mature cell
- It has high cellulose & less hemicelluloses content
IV) Tertiary cell wall
- Laid down on secondary wall
- Found in tracheids of gymnosperms
What is Pits?
- Cell wall is not uniform in thickness throughout
- Certain places cell wall are not laid down, such places are called pits
Pits are of two types
I) Simple Pit
- Pit chamber is uniform in diameter
- Found in angiosperms
II) Bordered pit
- Pit chamber is flask shaped
- Found in gymnosperms
- Number of plasmodesmata or cytoplasmic strands are present in pit
Functions of cell wall
- Maintains shape of the cells
- Protects cell from mechanical injury
- Allows materials to pass in and out of the cell
- Prevents undue expansion of cell when water enters by osmosis


2 thoughts on “Cell Wall Structure and Function | Free Biology Notes”