In this article we will discuss about habitat of algae:- 1. Aquatic habitat of algae, 2. Terrestrial habitat of algae and 3. Unusual habitat of Algae
- Algae are found everywhere on the earth, in air, water, and soil.
- Based on habitat the algae categorized as: Aquatic algae, Terrestrial algae and unusual habitat of algae.
1. Aquatic Habitat of Algae
- Majority of algae are aquatic.
- Found submerged or floating on water surfaces.
- Aquatic algae can be further divided into fresh water algae and marine algae
I. Fresh water algae
- Numerous types of algae are found in fresh water habitats like pool, ponds, lake, ditches or slow running river.
- Types of freshwater algae: Phytoplankton, Charophytes and Filamentous Algae
A. Phytoplankton
- Microscopic and free floating algae.
- They form the basis of freshwater food webs and contribute to oxygen production.
- E.g. Diatoms (Cyclotella, Fragilaria), Green Algae (Chlamydomonas, Scenedesmus) and Cyanobacteria (Microcystis, Anabaena)
B. Charophytes
- Charophytes are a group of green algae found in freshwater habitats.
- They can form dense meadows in lakes and ponds, providing habitat and food for various organisms.
- E.g. Chara, Nitella, Spirogyra
C. Filamentous Algae
- Filamentous algae, such as Spirogyra and Cladophora, are common in freshwater bodies
- They form green mats or long filaments in lakes, rivers, and streams.
- E.g. Spirogyra, Cladophora, Oedogonium

II. Marine algae
- Marine algae are found in salty water of sea and oceans.
- Generally, the members of phaeophyceae, Rhodophyceae and some Chlorophyceae are found in marine water.
- Types of marine algae: Phytoplankton and Seaweeds
A. Phytoplankton
- Microscopic algae, float near the surface, harnessing sunlight for photosynthesis.
- Phytoplankton form the foundation of marine food chains and contribute significantly to global oxygen production.
- E.g. Diatoms (Skeletonema, Thalassiosira), Dinoflagellates (Karenia, Alexandrium), Cyanobacteria (Prochlorococcus, Synechococcus)
B. Seaweeds
- They are macroalgae, commonly known as seaweeds
- They attach to rocks or other substrates along the coast or in the intertidal zone.
- Seaweeds can be further classified into three groups based on their color: green, brown, and red algae
- E.g. Green algae (Ulva, Enteromorpha), Brown algae (Fucus, Sargassum) and Red algae (Porphyra, Corallina)

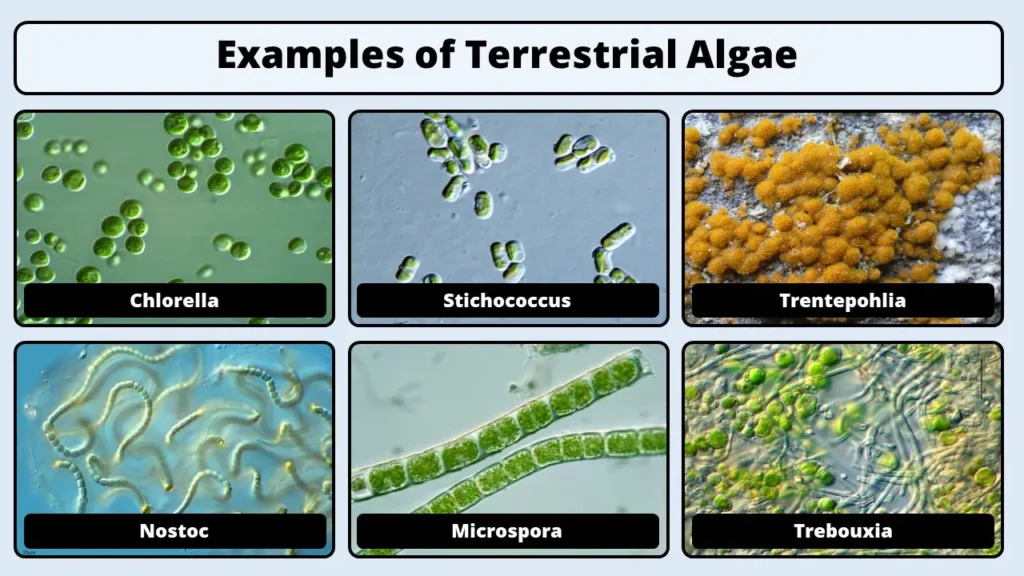
2. Terrestrial Habitat of Algae
- Those algae which are found in soil are termed as terrestrial algae.
- Types of Terrestrial algae: Soil Algae and Epiphytic Algae
I. Soil Algae
- They are present in soil ecosystems
- These algae are either found on the surface of the soil (saprophytes) or beneath the soil surface (cryptophytes).
- Soil algae contribute to nutrient cycling and soil stability.
- E.g. Chlorella, Nostoc, Stichococcus
II. Aerial Algae
- Some algae grow as epiphytes on plants, trees, or other surfaces
- They form green or colorful coatings on the surface of leaves, bark, or rocks.
- Epiphytic algae can be found in a variety of terrestrial habitats, including forests, wetlands, and deserts.
- E.g. Trentepohlia (found on tree trunks and rocks), lichenized algae (Trebouxia)
3. Unusual habitat of Algae
Such algae are found in habitats other than water or soil.
There are several types of unusual habitats:
I. Thermophytic algae
- The algae occurring in hot water springs at a very high temperature (70 degree or above) are thermophytic algae
- E.g. Oscillatoria brevis, Synechococcus elongates, Mastigocladus, Haplosiphon lignosum
II. Cryophytic algae
- Algae can survive in cold environments, including polar regions and high-altitude areas.
- Cold-adapted species, such as snow algae and Antarctic algae, can withstand freezing temperatures and limited light availability.
- E.g. Chloromonas, Chlamydomonas nivalis (snow algae), Prasiola (found in Antarctic and Arctic regions)
III. Halophytic algae
- Algae can inhabit brackish environments, such as estuaries and coastal marshes, where freshwater mixes with seawater.
- Halophytic algae are adapted to high salinity conditions and can be found in salt marshes, salt flats, and hypersaline lakes.
- Eg: Dunaliella (found in hypersaline environments), Salicornia (halophytic green algae), Halimeda (marine green algae found in coastal habitats)
IV. Epiphytic algae
- These algae grow on other aquatic plants
- E.g., Oedogonium, Aphanochaete, Bulbochaete, etc.
V. Endophytic algae
- These algae are found inside the higher plants.
- Nostoc is found in the thallus of Anthoceros, and Anabaena grows inside the coralloid roots of Cycas
VI. Epizoic algae
- Many algae grow on the shells of mollusks, turtles and fins of fishes and are known as epizoic algae.
- Cladophora is found on snails and shells of bivalves, Protoderma and Basicladia are found growing on back of turtles.
VII. Endozoic algae
- Endozoic algal cells are found inside the body of aquatic animals.
- E.g. Zoochlorella is found inside the Hydra.
VIII. Parasitic algae
- The best example of parasitic algae is Cephaleuros virescens causing red rust of tea (Camelia sinensis).
- Polysiphonia festigata is reported as semiparasite on Ascophyllum nodosum.
IX. Symbiotic algae
- Several members of Cyanophyceae (Cyanobacteria) grow in association with other plants.
- Lichen serves as the best example of symbiosis in which fungi from Ascomycetes and Basidiomycetes grow together with members of Cyanophyceae.

