Table of Contents
Blood Group: Definition, ABO and Rh Blood Group System
In this article, we will discuss the blood group system: ABO and Rh Blood group System
- Blood group system were discovered by Carl Land Steiner.
- Human beings have more than 30 types of antigens on the surface of blood cells.
- Chemicals that can induce immune response is called antigens.
- Antibodies are proteins that protect you when an unwanted substance enters your body.
- Various types of grouping of blood has been done.
- Two such groupings of blood
- ABO grouping
- Rh grouping
1. ABO Blood Group Sytem
- ABO grouping is based on the presence or absence of two surface antigens on the RBCs namely A and B.
- Similarly, the plasma of different individuals contain two natural antibodies
- During mis-matching of blood, the recipients immune system recognises the antigen on donors
- RBC and causes clumping (agglutination) of RBCs
- O group persons are called universal donors as they can donate blood to persons with any blood group.
- AB group persons are called universal recipients because they can accept blood from all groups.
2. Rh Blood Group System
- Landsteiner and Weiner (1940) discovered another protein on the surface of red blood corpuscles of rhesus monkey and many human beings. They called it as Rh factor or Rh-antigen.
- Nearly 80 percent of humans possess this factor and are Rh positive (Rh+)
- Others who do not have this factor are known as Rh negative (Rh–)
- Rh positive and Rh negative individuals are normal. The problem arises when an Rh-ve person is exposed to Rh+ve blood during blood transfusion or pregnancy.
Rh Incompatibility: Erythroblastosis foetalis
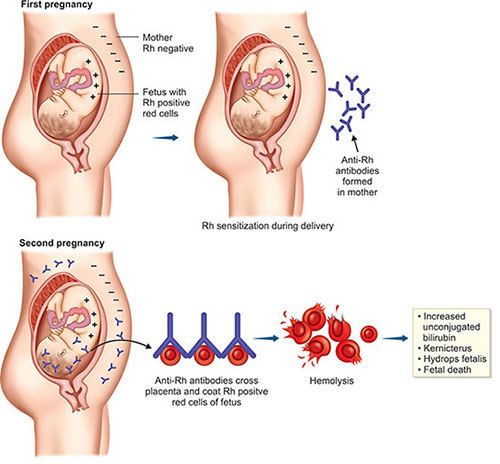
- A special case of Rh incompatibility has been observed between the Rh–ve blood of a pregnant mother and Rh+ blood of the foetus.
- Rh antigens do not get mixed with maternal blood in first pregnancy because placenta separates the two bloods.
- But at the time of first delivery, there is a possibility of exposure of the maternal blood to small amounts of the Rh+ve blood from the foetus.
- This induces the formation of Rh antibodies in maternal blood.
- In case of her subsequent pregnancies, Rh antibodies from mother leak into the foetal blood (Rh+ve) and destroy the foetal RBCs.
- This is fatal to foetus or cause severe anaemia and jaundice to the baby. This condition is called Erythroblastosis foetalis.
- Erythroblastosis foetalis can be avoided by administering anti-Rh antibodies to the mother immediately after the delivery of first child.
- Rh antibodies are given to mother with 72 hrs to destroy foetal RBC which prevent Rh-antibodies formation in mother.
READ MORE: