Blog
Frog Morphology Short Notes | Free Biology Notes
In this article we will discuss about the Frog Morphology
Frog Morphology
- Rana tigrina is the most common species of frog
- They are poikilotherms or cold blooded
- Frog is almost cosmopolitan nearby watery areas
- Frogs use camouflage to avoid predators
- The summer sleep of the frog is known as aestivation
- The winter sleep of the frog is known as hibernation
- The sound made by the male frog during breeding season is called croaking. It is a call for mating
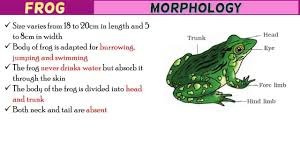
- Size varies from 18 to 20cm in length and 5 to 8cm in width
- Body of frog is adapted for burrowing, jumping and swimming
- The frog never drinks water but absorb it through the skin
- The body of the frog is divided into head and trunk
- Both neck and tail are absent
Head
- Head is triangular & its anterior conical part is called snout
- Two openings are present tip of snout is called nostrils
- Pair of nostrils helps in respiration
- On top of head pair of eyes are present. In eyes upper eyelid is immovable, lower eyelid is freely moveable and nictitating membrane arises from lower eyelid
- Frog lacks external ear. The ear drum or tympanum is present behind and below each eye
- In male vocal sacs are present, croaking during breeding season
Trunk
- Head is broadly joined behind with the flat trunk
- Two pairs of limbs are attached to its trunk
Fore limb
- The fore limb is shorter than the hind limb
- Fore limbs that end in four digits
- In male frog ventral side of first digit copulatory pad enlarge during breeding season
- This pad help the male frog to grip the female during copulation
Hind limb
- They are larger and muscular
- The hind limbs end in five digits
- They have webbed digits that help in swimming

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months ago[PPT] Human Reproduction Class 12 Notes
- Blog8 months ago
Contribution of Indian Phycologists (4 Famous Algologist)
- Blog8 months ago
PG TRB Botany Study Material PDF Free Download

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoCell The Unit of Life Complete Notes | Class 11 & NEET Free Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months ago[PPT] The living world Class 11 Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoPlasma Membrane Structure and Functions | Free Biology Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoJulus General Characteristics | Free Biology Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoClassification of Algae By Fritsch (11 Classes of Algae)













