Blog
Cockroach Reproductive System Short Notes | Free Biology Notes
In this article we will discuss about the cockroach reproductive system
Cockroach Reproductive system
- All characters of sexual dimorphism in cockroach present in abdomen
- In male, in addition of anal cerci, 9th sternum bears anal style (unjointed thread like) which are absent in females
- Cockroach are sexual dimorphism. Male and female are separate.
Male Cockroach Reproductive System
- The male cockroach reproductive system of cockroach consists of a pair of testes, vasa deferentia, an ejaculatory duct, utricular gland, phallic gland and external genitalia
Testes
- A pair of three lobed testis located on lateral side in 4-6 abdominal segments
- Testis produces sperms
- Testes become non functional in old adults
Vasa deferentia
- From each testis arises a thin thread-like tube is called vasa deferens
- Both the vasa deferentia meet in the middle and open into an ejaculatory duct
Ejaculatory duct
- Ejaculatory duct is an elongated wide duct
- Opens out by male gonopore situated ventral to the anus
Mushroom gland or utricular
- Large accessory reproductive gland
- Mushroom gland is present in the 6th and 7th abdominal segments of male cockroach
- Located at the junction of vasa deferentia with the ejaculatory duct
- It has a three types of glandular tubules
- Utriculi majores: peripheral long tubules
- Utriculi breviores: small short central tubules
- Seminal vesicles: behind the short central tubules are some short but more bulbous tubules filled with sperms
- Function of these gland is forms inner layer of spermatophore and nourishment to the sperms
Phallic or conglobate gland
- Long and club-shaped accessory gland
- Phallic duct open by a separate aperture
- Involved in the formation of the spermatophore
External genitalia
- Surrounding the male genital pore in the genital pouch there are three chitinous plates called phallomeres
- The phallomeres together constitute the phallic organs or gonapophyses
- These organ help for copulation
Spermatophore
- Sperm produced in testes are stored in seminal vesicle
- All sperms released from seminal vesicles glued together to form a ball called sperm ball
- Long tubules of mushroom gland secrete a membrane around sperm ball called spermatophore
- Small tubules secrete a nutritive fluid in spermatophore
- At the time of copulation spermatophore enters into ejaculatory duct
- Ejaculatory duct secrete another coat on spermatophore and hence it becomes double layered
- When it is released outside from male genital pore then phallic gland secretes another layer, so spermatophore becomes three layered
- They are finally discharged during copulation
Female Cockroach Reproductive System
Ovaries
- One pair of ovaries are situated in 2nd to 6th segments
- Each ovary consists of 8 blind ovarian tubules or ovarioles
- Inside ovarioles series of ova are situated in an acropetal order
Oviducts
- Ovarioles of ovary unite to form short and wide lateral oviduct
- Two lateral oviducts join to form a median common oviduct or vagina in the 7th segment
Vagina
- Posterior wider part of the common oviduct
- Vagina opens into a large genital pouch by female genital pore on the 8th sternum
Genital pouch
- Genital pouch is formed by the 7th, 8th and 9th sternites
- Genital pouch can be divided into two parts
- Genital chamber: anterior part containing female gonopore and pores of spermathecae and collateral glands
- Vestibulum: larger posterior part in which ootheca is formed
Collaterial glands
- A pair of branched accessory reproductive gland
- These glands open into the genital pouch by two separate openings
- The secretion of collateral glands helps in the formation of ootheca
Spermathecae
- A pair of unequal sized spermatheca are associated with genital chamber
- Spermathecae opens into the genital chamber on a small spermathecal papilla
- Responsible for receiving, maintaining, and releasing sperm to fertilize eggs
External genitalia of female
- Situated between the female genital pore and anus inside the genital pouch there are 3 pairs of chitinous plate like structures called gonapophyses or pallomeres
- These gonapophyses help in copulation, egg-laying and in the formation of ootheca.
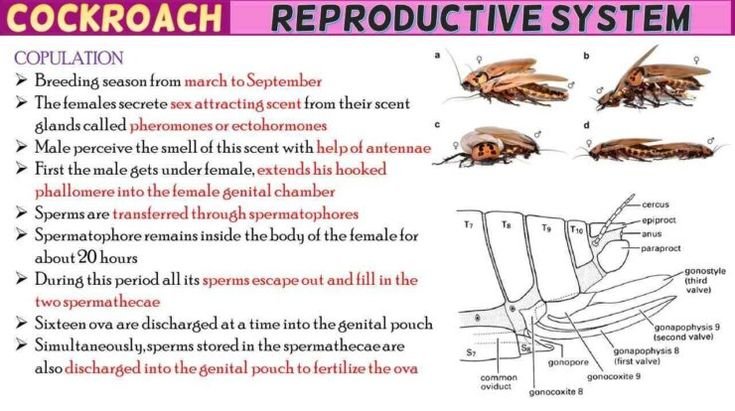
Copulation
- Breeding season from march to september
- The females secrete sex attracting scent from their scent glands called pheromones or ectohormones
- Male perceive the smell of this scent with help of antennae
- First the male gets under female, extends his hooked phallomere into the female genital chamber
- Sperms are transferred through spermatophores
- Spermatophore remains inside the body of the female for about 20 hours
- During this period all its sperms escape out and fill in the two spermathecae
- Sixteen ova are discharged at a time into the genital pouch
- Simultaneously, sperms stored in the spermathecae are also discharged into the genital pouch to fertilize the ova
Fertilization
- Fertilization is internal
- Fertilized eggs become hardened by the secretion of colleterial glands, which hardens to form an ootheca
- Ootheca is a dark reddish to blackish brown capsule
- They are dropped or glued to a suitable surface
- Development of egg takes place inside ootheca
- Development is indirect, meaning there is development through nymphal stage
- The nymphs look very much like adults, the nymph grows by moulting about 13 times to reach the adult form.
- Nymph changes into an adult in 1 year

 Blog5 months ago
Blog5 months ago[PPT] Human Reproduction Class 12 Notes
- Blog5 months ago
PG TRB Botany Study Material PDF Free Download

 Blog5 months ago
Blog5 months ago[PPT] The living world Class 11 Notes

 Blog5 months ago
Blog5 months agoCell The Unit of Life Complete Notes | Class 11 & NEET Free Notes
- Blog5 months ago
Contribution of Indian Phycologists (4 Famous Algologist)

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoIbomma Bappam: Redefines Telugu Streaming Trend
- Blog5 months ago
Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter wise PPT
- Blog5 months ago
Class 10 Biology Notes Chapter wise PPT