Blog
Internal Structure of Dicot Stem Notes | Free Biology Notes
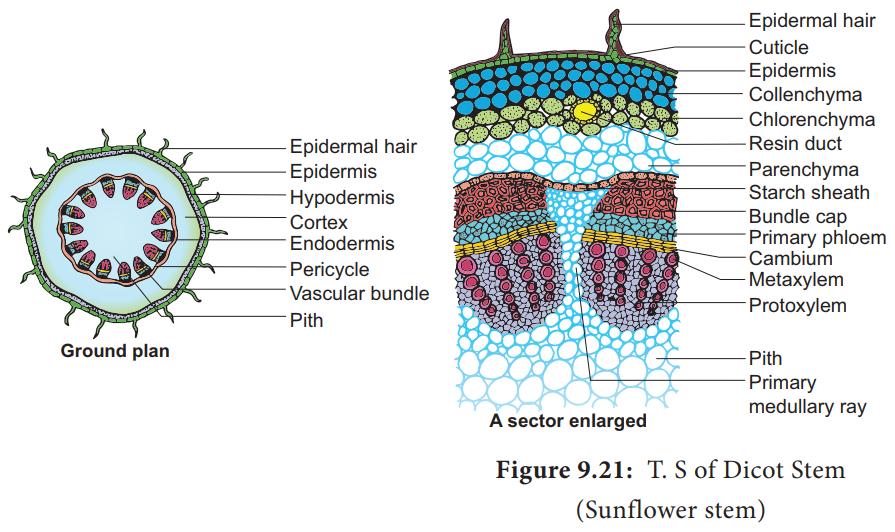
This article we will discuss about Internal Structure of Dicot Stem
The transverse section of a dicot stem reveals the following structures
Epidermis
- Epidermis is a outermost layer and made up of parenchymatous cells
- Cuticle a protective layer, covers this layer
- It possesses stomata and large number of multicellular hairs
- Epidermis has following functions: Minimize the rate of transpiration, protects from mechanical injury, prevents the entry of harmful organisms and helps in the exchange of gases through stomata
Hypodermis
- Present below the epidermis & multilayered of collenchymatous cells
- Hypodermis has following functions: provides mechanical strength, perform photosynthesis and storage of food
Middle cortex
- Present below the hypodermis & made up of oval cells of parenchyma
- In some plants contains oil ducts & Resin canals
- Middle cortex has following functions: Storage of food & perform photosynthesis
Endodermis
- Its separates the cortex from vascular bundles
- Cells are barrel shaped, compactly arranged, having no intercellular spaces and are parenchymatous.
- Due to abundant starch grains, this layer is also known as starch sheath
- Casparian strips are absent in stem
- Endodermis has following functions: serve for storage of food
Pericycle
- Pericycle is present below the endodermis and composed of sclerenchymatous and parenchymatous cells
- Sclerenchyma forming like a cap on the bundle, so called as bundle caps.
- Parenchymatous present between the two bundles
- Pericycle has following functions: mechanical support and serves to store food
Vascular bundles
- These are arranged in a ring and inner to the pericycle
- Vascular bundle is conjoint, collateral, open type
- Vascular bundles are made up of: xylem, phloem and cambium
- Xylem – helps in conduction of sap
- Phloem – conducts the foods
- Cambium – lies in between xylem and phloem and responsible for secondary growth
Pith
- Occupies central portion of the stem
- Composed of thin walled parenchymatous, rounded or polygonal, with or without intercellular spaces
- The extension of pith between vascular bundles are called as pith ray or medullary rays.
- Pith has following functions: food is stored in this region.

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months ago[PPT] Human Reproduction Class 12 Notes
- Blog8 months ago
Contribution of Indian Phycologists (4 Famous Algologist)
- Blog8 months ago
PG TRB Botany Study Material PDF Free Download

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoCell The Unit of Life Complete Notes | Class 11 & NEET Free Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months ago[PPT] The living world Class 11 Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoPlasma Membrane Structure and Functions | Free Biology Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoJulus General Characteristics | Free Biology Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoClassification of Algae By Fritsch (11 Classes of Algae)













