Blog
Phylum Cnidaria: General Characteristics and Classification | 100% Free Biology Notes
After reading this article you will learn about Phylum Cnidaria: General Characteristics and Classification.
Habit & Habitat
- Aquatic (mostly marine and few fresh water)
- Sessile or free swimming
- Solitary or colonial
Cnidaria General Characteristics
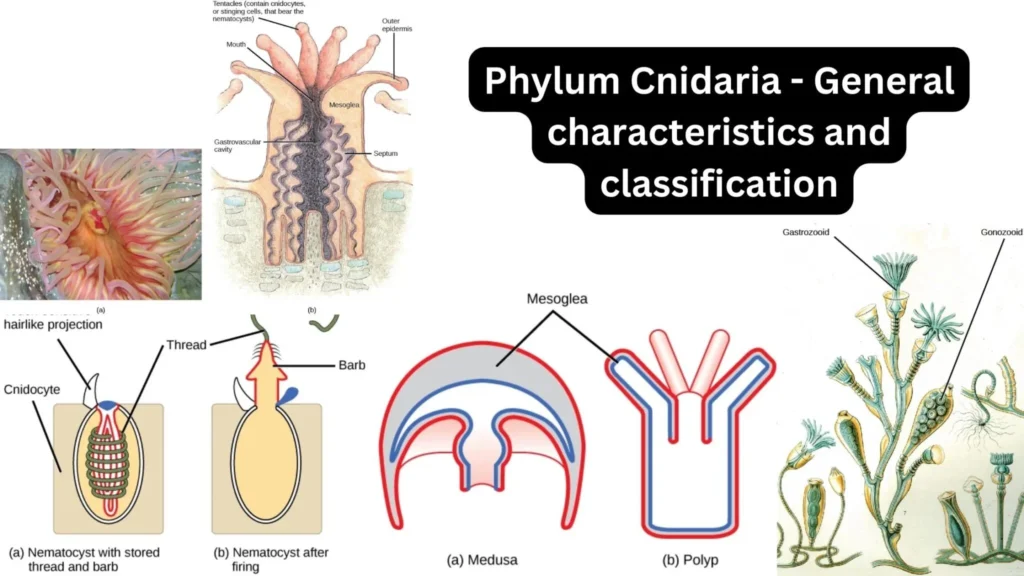
- Coelenterates are also known as Cnidaria due to presence of stinging cells called Cnidoblast
- Cnidarians composed of two layers of tissue known as ectoderm and endoderm with non cellular layer called mesogloea in between
- Epidermis is made of muscular cells, cnidoblasts, sensory cells, nerve cells and germ cells
- Gastrodermis is inner lining of the gastrovascular cavity. It is a single-layered tissue with gland cells
- and phagocytic nutritive cells
- Basic body shape of cnidarians consists of sac with gastrovascular cavity or coelenteron with a single opening
- Tentacles are finger like structures which surrounds the mouth of coelentreates
- Tentacles are used for food capture and defense
- Cnidoblasts are stinging cells with a poison filled capsule called nematocyst
- It contains a poisonous substance called hypnotoxin
Body Forms of Cnidaria
I) Polyp
- Cylindrical and sessile form
- Mouth and Tentacles directed upward
- May be Solitary or Colonial
- E.g. Hydra and Adamsia
II) Medusa
- Umbrella shaped and free swimming
- Always solitary
- Mouth and Tentacles directed downward
- E.g. Aurelia
Reproduction in Cnidaria
- Asexual by Budding
- Sexual by production of gametes
- Development is indirect
- Alternation of generation:- Its also known as metagenesis. This phenomenon shown by some cnidarians in which polyps produce medusa asexually and medusa form the polyps sexually. E.g. Obelia
Classification of cnidaria
Class 1. Hydrozoa
- Both polyp and medusa stage present
- Medusa with a velum
- Fresh and marine water
- E.g. Hydra, Obelia and physalia
Class 2. Scyphozoa
- Medusa stage dominant
- Polyp reduced or absent
- Medusa without velum
- E.g. Aurelia
Class 3. Anthozoa
- All polyps
- No medusa stage
- This class has two types of animals
- Sea anemones:- Skeleton absent
- Corals:- CaCO3 Skeleton

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months ago[PPT] Human Reproduction Class 12 Notes
- Blog8 months ago
Contribution of Indian Phycologists (4 Famous Algologist)
- Blog8 months ago
PG TRB Botany Study Material PDF Free Download

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoPlasma Membrane Structure and Functions | Free Biology Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoCell The Unit of Life Complete Notes | Class 11 & NEET Free Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months ago[PPT] The living world Class 11 Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoJulus General Characteristics | Free Biology Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoClassification of Algae By Fritsch (11 Classes of Algae)