Blog
Fluid Mosaic Model of Plasma Membrane | Class 11 & NEET Free Notes
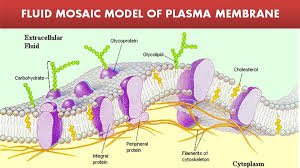
In this article we will discuss about:- What is Fluid Mosaic Model?, Components of Plasma Membrane, Role of the components of Plasma Membrane and Functions of Plasma Membrane
What is Fluid Mosaic Model of Plasma Membrane?
- Fluid mosaic model was proposed by S.J. Singer and Garth L. Nicolson
- This model explains the structure of the plasma membrane
- Plasma membranes made up of phospholipids, proteins, cholesterol, and carbohydrates
- These components give a fluid character to the membranes
- Cholesterol and proteins are embedded in the bilayer that gives the membrane a mosaic look
Components of Plasma Membrane
- Phospholipid: The main fabric of plasma membrane
- Proteins: Inner or outer and embedded within phospholipid layers
- Cholesterol: Between phospholipids and phospholipid bilayers
- Carbohydrates: Attached to proteins on outside membrane layers
Role of the components of Plasma Membrane
Phospholipids
- Phospholipids Have a hydrophobic head and fatty acid tail, form a bilayer separating the cell from the outside.
- They are fluid and components can move around freely
- Permeable to small and non-polar molecules
- Impermeable to large molecules and ions and prevent these substances from passing thorough
Proteins
- The plasma membrane has three types of proteins:
- Integral Proteins: These proteins form channels to allow the movement of large molecules and ions across the hydrophobic layer of the membrane.
- Peripheral Proteins: These are found embedded in a single leaflet of the membrane. They carry signals from one segment of the membrane and relay it to another.
- Glycoproteins: They stabilize the membrane and are responsible for intercellular communication.
Cholesterol
It helps the plasma membrane to retain the fluidity. It is present between the phospholipids and prevents the compaction of hydrophilic tails at low temperatures and their expansion at high temperatures.
Functions of Plasma Membrane
- Structural, keeping the cell contents together
- Separate cell components from the outside environment
- Allows cells to communicate with each other by cell signalling
- Allows recognition of other external substances
- Allows mobility in some organisms, e.g. amoeba
- Selectively permeable barrier
- Regulating the transport of materials into or out of cells
- The site of various chemical reactions

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months ago[PPT] Human Reproduction Class 12 Notes
- Blog8 months ago
Contribution of Indian Phycologists (4 Famous Algologist)
- Blog8 months ago
PG TRB Botany Study Material PDF Free Download

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoCell The Unit of Life Complete Notes | Class 11 & NEET Free Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months ago[PPT] The living world Class 11 Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoPlasma Membrane Structure and Functions | Free Biology Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoJulus General Characteristics | Free Biology Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoClassification of Algae By Fritsch (11 Classes of Algae)













