Blog
Internal Structure of Dicot Leaf Notes | Free Biology Notes
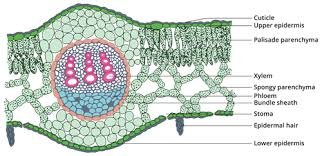
This article we will discuss about Internal Structure of dicot leaf
The transverse section of a Dicot leaf reveals the following structures
Epidermis
- A dicot leaf is generally dorsiventral
- It has upper and lower epidermis
I) upper epidermis
- Outermost layer present on the upper side of the leaf
- Upper epidermis is made up of a single layer of parenchymatous cells without intercellular spaces
- Thick cuticle layer is present on the upper epidermis
- Stomata are generally absent in the upper epidermis
II) lower epidermis
- Outermost layer present on the lower side of the leaf
- It is a single layer, parenchymatous & covered with cuticle
- Stomata are more on lower epidermis
- Chloroplasts present only guards cells of the epidermis
- Function of epidermis
- Protective layer
- Exchange of gases
- Facilitates the transpiration
Mesophyll tissue
- Present between upper and lower epidermis, there is an entire mass of ground tissue called mesophyll
- Consists of two different kinds of parenchyma cells
I) Palisade parenchyma
- Present below the upper epidermis
- Elongated parenchyma cells as they have more chloroplasts
- Helps in the process of photosynthesis
II) Spongy parenchyma
- Present below the palisade parenchyma tissue
- They are arranged irregularly with intercellular spaces
- Helps in gaseous exchange
Vascular bundle
- Vascular bundles occur at the midrib and veins of the leaf
- Vascular bundle is collateral and closed
- Vascular bundle consists of xylem and phloem
- They are surrounded by parenchyma is bundle sheath
- Functions of vascular bundle: conduct water and food materials

 Blog7 months ago
Blog7 months ago[PPT] Human Reproduction Class 12 Notes
- Blog7 months ago
PG TRB Botany Study Material PDF Free Download
- Blog7 months ago
Contribution of Indian Phycologists (4 Famous Algologist)

 Blog7 months ago
Blog7 months agoCell The Unit of Life Complete Notes | Class 11 & NEET Free Notes

 Blog7 months ago
Blog7 months ago[PPT] The living world Class 11 Notes

 Blog7 months ago
Blog7 months agoJulus General Characteristics | Free Biology Notes

 Blog7 months ago
Blog7 months agoClassification of Algae By Fritsch (11 Classes of Algae)
- Blog7 months ago
Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter wise PPT












