Blog
Plasma Membrane Structure and Functions | Free Biology Notes
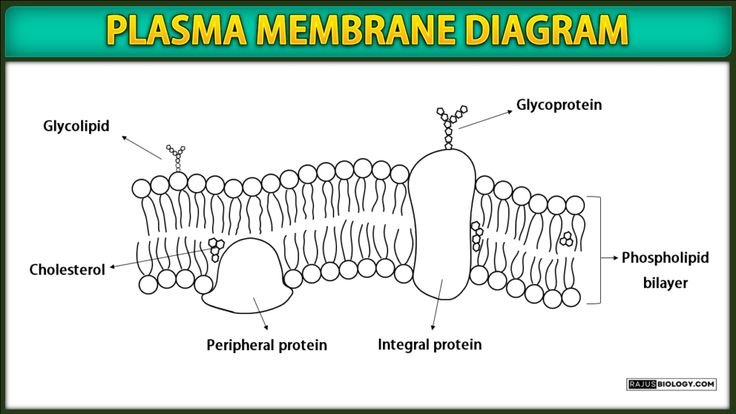
In this article we will discuss about:- Plasma Membrane Structure, Function of Plasma Membrane and Transport through Plasma Membrane
What is Plasma Membrane?
- Plasma membrane is thin, elastic semi permeable living membrane that serves as boundary for the cytoplasm
- Plasma membrane was coined by Nageli in 1855
- Also known as Cell membrane or plasmalemma
- Made up of protein and phospholipids
- Selectively permeable in nature
- Dynamic membrane
Plasma Membrane Structure
- Three important models explaining the structure of plasma membrane are
- Sandwiched model
- Unit membrane model
- Fluid mosaic model
1. Sandwiched Model
- In 1935, proposed by Davson & Danielli
- Oldest model on the structure of plasma membrane
- Plasma membrane is made up of three layers
- Outer protein layer, middle lipid layer & inner protein layer
- Proteins are alpha globular
- Lipids are amphipathic
- Lipids arranged in bilayer in such a manner that tails face each others
- Van der vaal force helping to 2 layers stay together
- Proteins on either side of phospholipids bilayers
2. Unit Membrane Model
- In 1959, Proposed by Robertson
- Plasma membrane is made up of three layers
- Outer protein layer, Middle lipid layer & inner protein layer
- Proteins are beta fibers
- Thickness of plasma membrane is 7.5nm (75Å)
- Lipids are amphipathic
- Lipids arranged in bilayer in such a manner that tails face each others
- Van der vaal force helping to 2 layers stay together
- Proteins on either side of phospholipids bilayers
3. Fluid Mosaic Model
- In 1972, Proposed by Singer & Nicolson
- Made up of protein and phospholipids
- Proteins are alpha globular & two types
I) Extrinsic Proteins
- Arranged on surface of lipid heads
- Loosely attached
II) Intrinsic Proteins
- Deeply embedded
- Tightly bound to lipids
Phospholipids have two types of movements
I) Transition
- Movement of phospholipids molecules in the same layer
Ii) Flip Flop
- Movement of phospholipids molecules between two layers
- Protein iceberg in a sea of phospholipids
Function of Plasma Membrane
a) Mechanical Support
- It gives shape to the cell
- Protects all cell contents
b) Exchange of Materials
- Regulate the exchange of materials
- It allows need materials to enter the cell
- It Send out unwanted materials from the cell
c) Endocytosis
- Engulfing of food or foreign particles through the
- Plasma membrane
- Endocytosis differentiated into two types
I) Phagocytosis
- Engulfing of solid particles through the plasma membrane
- g. Amoeba & WBC
II) Pinocytosis
- Engulfing of fluid particles through the plasma membrane
- E.g. Epithelial cells of intestine
d) Exocytosis
- Process of exudating secretary products from the cells to outside of the cytoplasm
- E.g. Pancreatic cells
[ Also Read: Cell Wall Structure and Function ]
Transport through Plasma Membrane
- I) Passive Transport
- No need ATP
- Movement of substance according to concentration gradient
- Higher concentration to lower concentration
Osmosis: Movement of solvent through selectively permeable membrane
Diffusion: Movement of molecules through selectively permeable membrane
Facilitated diffusion: Movement of molecules through transport protein in plasma membrane
Ii) Active Transport
- Need ATP
- Movement of substance against to concentration gradient
- Lower concentration to Higher concentration
- E.g. Na+/K+ Pump and Ca Pump etc.

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months ago[PPT] Human Reproduction Class 12 Notes
- Blog8 months ago
Contribution of Indian Phycologists (4 Famous Algologist)
- Blog8 months ago
PG TRB Botany Study Material PDF Free Download

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoCell The Unit of Life Complete Notes | Class 11 & NEET Free Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months ago[PPT] The living world Class 11 Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoJulus General Characteristics | Free Biology Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoClassification of Algae By Fritsch (11 Classes of Algae)

 Entertainment7 months ago
Entertainment7 months agokatmovie 18 Movies and Streaming Experience













