Blog
Sycon Diagram, Structure and Reproduction | Free Biology Notes
In this article we will discuss about sycon diagram, structure and reproduction
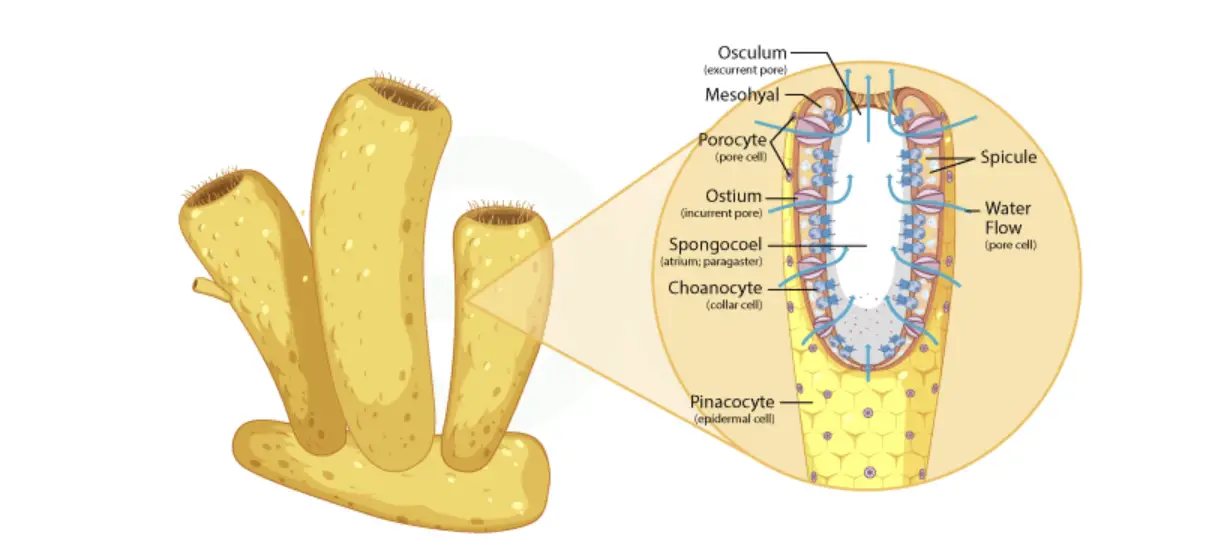
Structure of Sycon
Sycon is a type of sponge with the following structures:
- Osculum: It is an opening at the top of the sycon through which water exits the body.
- Amebocyte: They are specialized cells found within the body that play a role in digestion and transport of nutrients.
- Chonocyte (Collar cell): They are responsible for generating water currents and capturing food particles.
- Ostium: Ostia are small openings in the body wall of the sycon through which water enters the sponge.
- Porocyte: Porocytes are cells that line the ostia and regulate the flow of water into the body.
- Spongocoel: The spongocoel is the central cavity or chamber within the sycon where water circulates.
- Spicule: Spicules are needle-like structures made of calcium carbonate or silica that provide structural support to the sycon.
- Pinacocyte: Pinacocytes are thin, flat cells that make up the outer layer of the sycon and help protect the sponge’s internal structures.
Reproduction in Sycon
Sycon exhibits two types of reproduction: asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction. Here’s a simple explanation of each:
1. Asexual Reproduction:
In sycon, asexual reproduction can occur through three main methods: budding, fragmentation, and gemmules.
- Budding: The bud from and eventually detaches from the parent, becoming an independent organism.
- Fragmentation: Breaking of the parent into two or more fragments, each of which can develop into a new organism.
- Gemmules: Gemmules are specialized structures formed by sycon. They are resistant capsules or clusters of cells that contain all the necessary materials for developing into a new sponge. Gemmules can survive harsh conditions such as drying out or extreme temperatures, and they can later germinate, giving rise to new individuals when conditions become favorable again.
2. Sexual Reproduction:
Sexual reproduction in sycon involves the fusion of gametes, which are reproductive cells. They produces male and female gametes, which are released into the water. Fertilization occurs when the sperm from a male sycon sponge meets the eggs from a female sycon sponge, resulting in the formation of a zygote that develops into a new individual sponge.

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months ago[PPT] Human Reproduction Class 12 Notes
- Blog8 months ago
Contribution of Indian Phycologists (4 Famous Algologist)
- Blog8 months ago
PG TRB Botany Study Material PDF Free Download

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoPlasma Membrane Structure and Functions | Free Biology Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoCell The Unit of Life Complete Notes | Class 11 & NEET Free Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months ago[PPT] The living world Class 11 Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoClassification of Algae By Fritsch (11 Classes of Algae)

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoJulus General Characteristics | Free Biology Notes