Blog
Life Cycle Patterns of Algae (5 Types of Life Cycle in Algae)
In this article we will discuss about 5 life cycle patterns of algae (Life Cycle in Algae):- 1.Haplontic life cycle, 2.Diplontic life cycle, 3.Diplohaplontic life cycle, 4.Haplobiontic life cycle and 5.Diplobiontic life cycle
Types of Life Cycle in Algae
- The sequence of events through which one generation passes into the next generation is called life cycle.
- Sexual reproduction involves alternation between haploid and diploid generation which we call alternation of generation.
- In algae, there are five main types of life cycles or alternation of generation: haplontic life cycle, diplontic life cycle, diplohaplontic life cycle, haplobiontic life cycle and diplobiontic life cycle
1. Haplontic Life Cycle in Algae
- The haplontic life cycle is the simplest and most primitive life cycle pattern observed in some algae, particularly unicellular and filamentous forms.
- In this life cycle, the dominant and visible phase is the haploid gametophyte.
- Haploid gametophyte produces gametes through mitosis, which then fuse during sexual reproduction to form a diploid zygote.
- The zygote undergoes meiosis to produce haploid spores, which develop into new haploid individuals.
- Zygotic meiosis occurs, with no formation of a sporophytic thallus (diploid).
- E.g. Chlamydomonas, Oedogonium and spirogyra
2. Diplontic Life Cycle in Algae
- The diplontic life cycle is commonly found in higher plants but is also observed in certain algae. In this life cycle, the dominant and visible phase is the diploid sporophyte.
- The diploid sporophyte produces gametangium.
- In gametangium, the male and female gametes produced by meiosis.
- The gametes undergo syngamy to produce a diploid zygote.
- The zygote germinate into the sporophytic plant.
- The sporophytic plant will later undergo meiosis to produce the gametes.
- E.g. diatoms (Bacillariophyceae), Dasycladiales (green algae) and Fucales, Sargassum (Brown algae)
3. Diplohaplontic Life Cycle in Algae
- True alternation of generation occurs.
- This type of life cycle that consists of two different vegetative individuals alternating with each other is called diplohaplontic.
- There are two types of diplohaplontic life cycles
I. Isomorphic
- The diploid sporophyte produces sporangia. The sporangial mother cells undergo meiosis and produce haploid meiospores.
- The meiospores germinate into haploid gametophytic thalli and here gametes are produced. The male and female gametes fuse together to form a diploid zygote (2N). It produces diploid sporophytic thallus.
- Alternating sporophyte and gametophyte are morphologically similar.
- E.g., Ulvales, Cladophorales, Ectocarpales, Dictyotales and red algae.
II. Heteromorphic
- Alternating generations are morphologically dissimilar.
- E.g., Laminarials, Desmarestiales etc
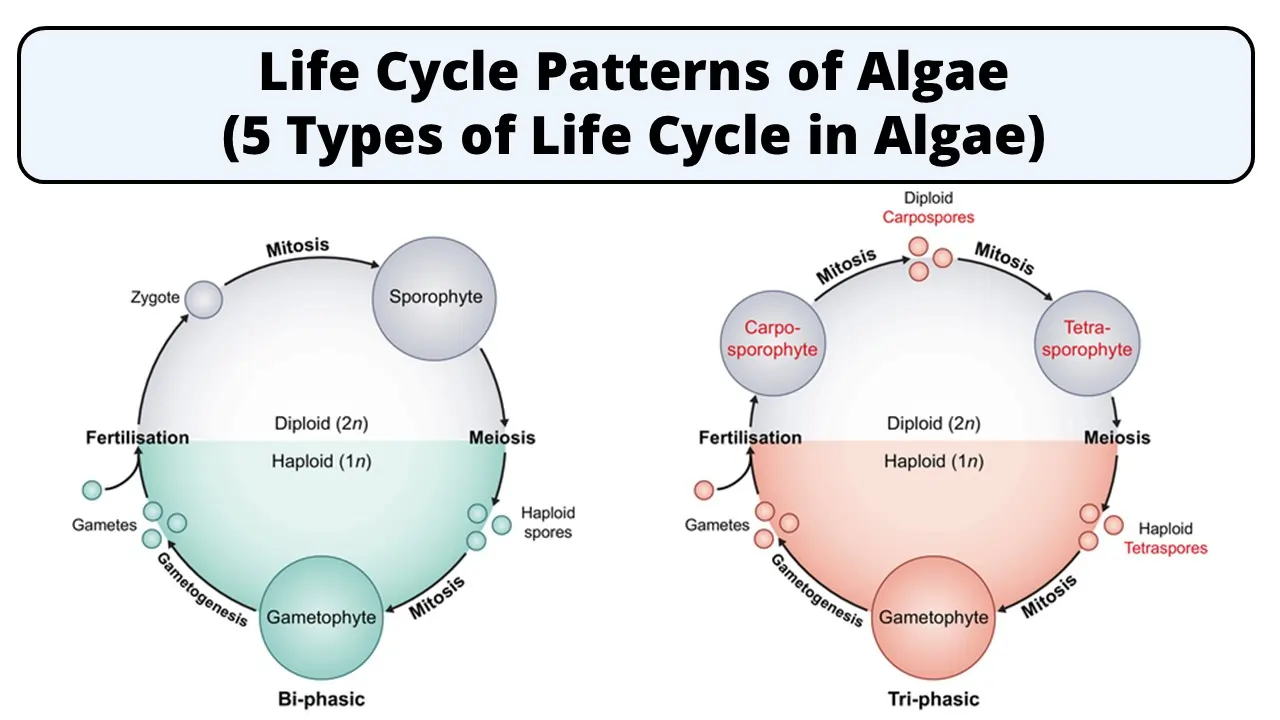
4. Haplobiontic Life Cycle in Algae
- In this life cycle two haploid generations alternate with one diploid generation (Triphasic life cycle).
- The two haploid generations are represented by the carposporophyte and the gametophyte.
- The diploid sporophytic phase is restricted to zygote (2N).
- The main plant body which is gametophyte produces gametes. These gametes fuse to form zygote that undergoes meiosis and develops into carposporophyte.
- Carpospores of carposporophyte germinates to form chatransia stage.
- Chatransia stage then develops into normal gametophyte.
- E.g. Batrachospermum (red alga), Nemalion
5. Diplobiontic Life Cycle in Algae
- In this life cycle one haploid generations alternate with two diploid generation.
- The main plant body is gametophyte that produces gametes.
- Zygote is formed by syngamy and differentiates into diploid carposporophyte.
- Diploid carposporangia develops in carposporophyte and diploid carpospores are produced within carposporangia.
- On liberation, carpospores develops into diploid tetrasporophyte.
- Tetraspores are produced after meiosis inside tetrasporangia.
- Tetraspores develop into main gametophytic plant thallus.
- E.g. Polysiphonia

 Blog4 months ago
Blog4 months ago[PPT] Human Reproduction Class 12 Notes
- Blog4 months ago
PG TRB Botany Study Material PDF Free Download

 Blog4 months ago
Blog4 months ago[PPT] The living world Class 11 Notes

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoIbomma Bappam: Redefines Telugu Streaming Trend
- Blog4 months ago
Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter wise PPT
- Blog4 months ago
Contribution of Indian Phycologists (4 Famous Algologist)

 Blog4 months ago
Blog4 months agoDownload NEET Biology Study Materials in Tamil

 Blog4 months ago
Blog4 months agoCell The Unit of Life Complete Notes | Class 11 & NEET Free Notes