In this article we will discuss about difference between leucoplast and chloroplast
Difference Between Leucoplast and Chloroplast
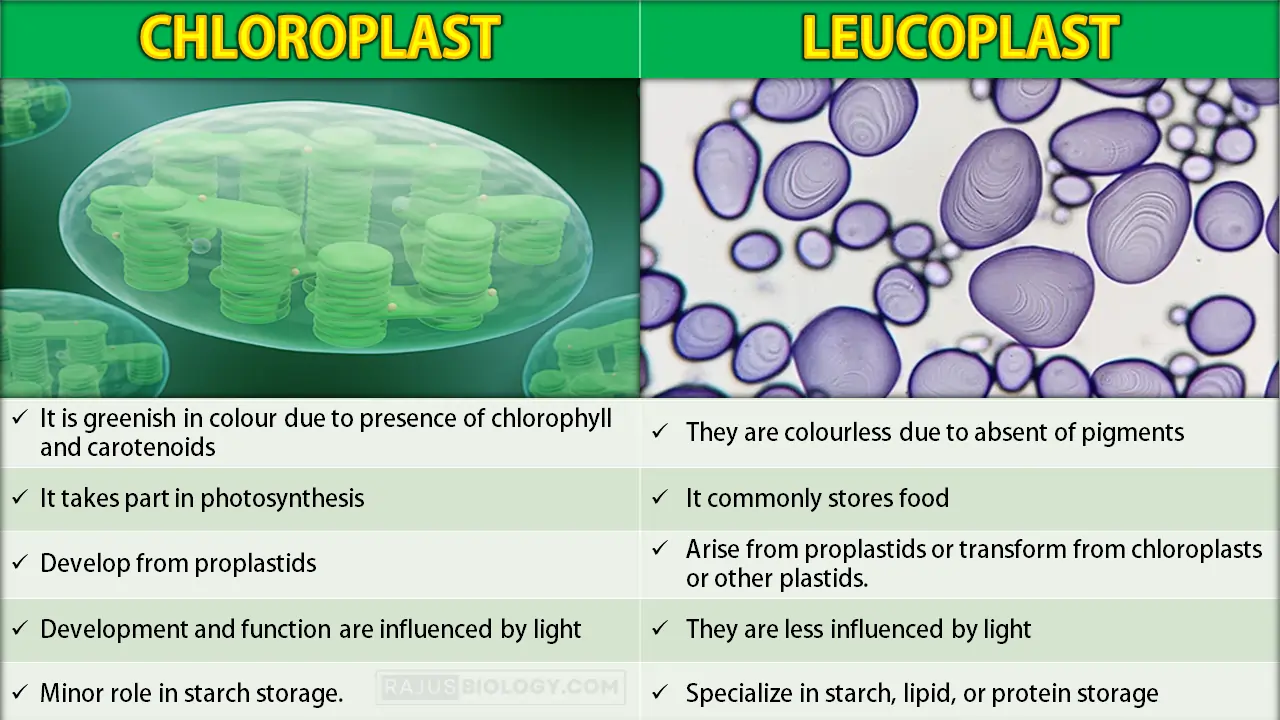
1. Pigment Content: Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll pigments, which give them a green color and are essential for photosynthesis. Leucoplasts, on the other hand, lack chlorophyll and do not possess any pigments.
2. Function: Chloroplasts are primarily involved in photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into chemical energy. Leucoplasts, however, have various functions depending on their specific type, such as storage of starch, lipids, or proteins, synthesis of fatty acids, or production of pigments in some specialized cells.
3. Membrane Structure: Chloroplasts have a complex internal membrane system consisting of thylakoid membranes, which are stacked into grana, and the stroma lamellae. Leucoplasts, in contrast, have simpler membrane structures without the extensive internal membrane system found in chloroplasts.
4. Pigment Storage: Chloroplasts store pigments, particularly chlorophyll, within their thylakoid membranes. Leucoplasts lack pigments and do not serve as sites for pigment storage.
5. Photosynthetic Machinery: Chloroplasts contain all the necessary components for photosynthesis, including photosystems, electron transport chains, and ATP synthase enzymes. Leucoplasts lack these components since they are not involved in photosynthesis.
6. Starch Storage: Some types of leucoplasts, known as amyloplasts, specialize in storing starch. They contain enzymes involved in starch synthesis and serve as the primary site for starch accumulation in plant cells. Chloroplasts, on the other hand, play a minor role in starch storage compared to amyloplasts.
7. Lipid and Protein Storage: Different types of leucoplasts, such as elaioplasts and proteinoplasts, are involved in the storage of lipids and proteins, respectively. Chloroplasts do not primarily serve as sites for lipid or protein storage.
8. Development: Chloroplasts develop from proplastids, which are undifferentiated plastids found in young plant cells. Leucoplasts can arise from proplastids or can be derived from the transformation of chloroplasts or other plastids, depending on the specific needs of the cell.
9. Environmental Influence: Chloroplast development and function are influenced by light conditions. They are more abundant and active in cells exposed to light. Leucoplasts, however, are less influenced by light and can be present in cells regardless of light exposure.
10. Pigmentation: Chloroplasts give plant tissues their green color due to the presence of chlorophyll pigments. Leucoplasts, lacking pigments, are colorless and do not contribute to the pigmentation of plant tissues.
Summary: Difference Between Leucoplast and Chloroplast
- Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll pigments and are involved in photosynthesis, while leucoplasts lack pigments and have various functions depending on their type.
- Chloroplasts have a complex internal membrane system, while leucoplasts have simpler membrane structures.
- Chloroplasts store pigments and are involved in photosynthetic processes, while leucoplasts do not serve as sites for pigment storage and are not involved in photosynthesis.
- Leucoplasts specialize in starch, lipid, or protein storage, while chloroplasts play a minor role in starch storage.
- Chloroplasts develop from proplastids, while leucoplasts can arise from proplastids or transform from chloroplasts or other plastids.
- Chloroplasts’ development and function are influenced by light, while leucoplasts are less influenced by light and can be present in cells regardless of light exposure.
- Chloroplasts give green color to plant tissues, while leucoplasts are colorless.
Read More:
Cell Biology Notes


![[PPT] The living world Class 11 Notes](https://rajusbiology.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/06/PPT-The-living-world-Class-11-Notes-300x169.webp)
