Blog
Endoplasmic Reticulum Structure, Types and Functions | Class 11 & NEET Free Notes
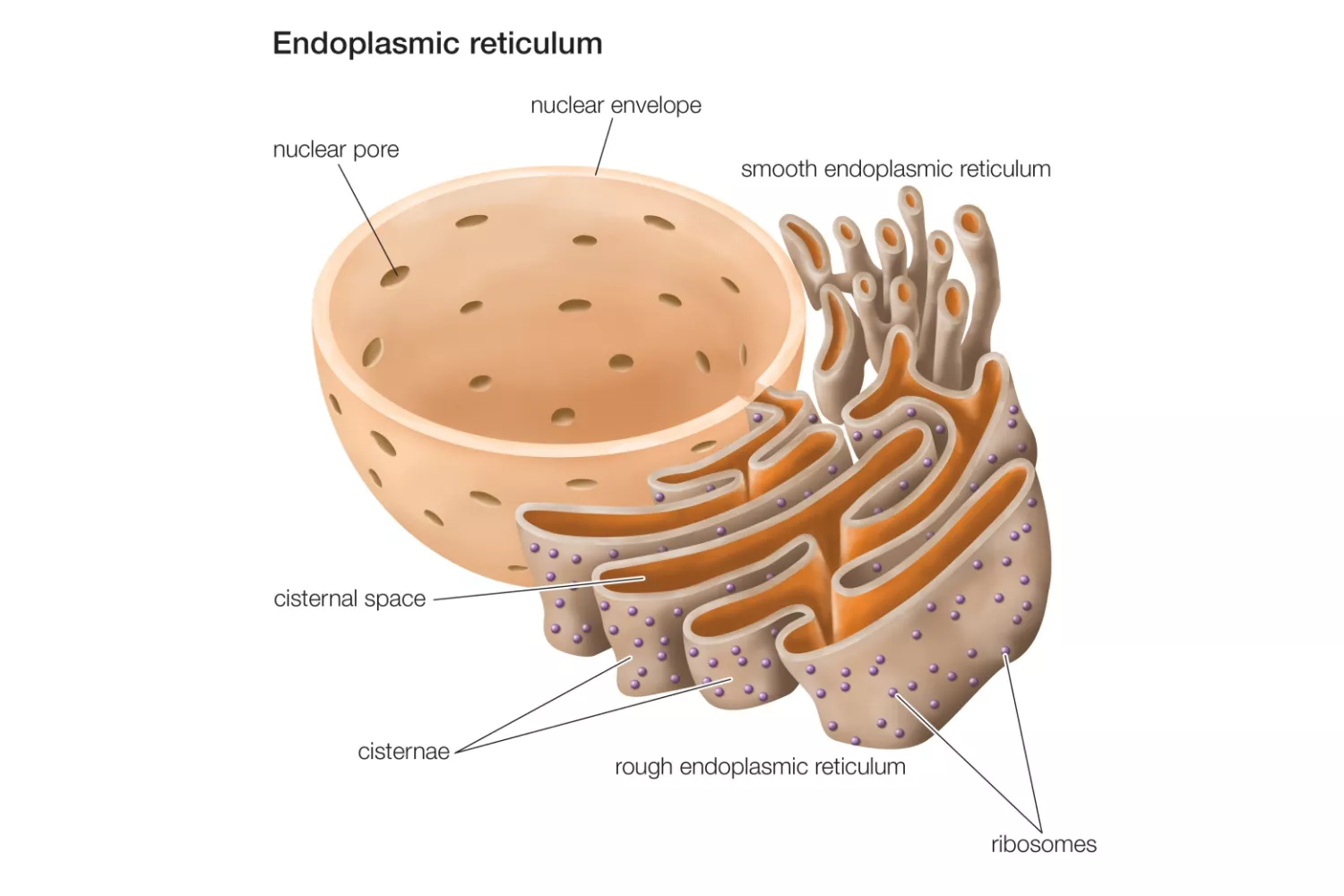
In this article we will discuss about:- Endoplasmic Reticulum Structure, Types and Functions
- In 1897, observed by Garnier and named it as ergastoplasm
- In 1945, first described by Porter, Claude and Fullman
- In 1953, term given by porter
- Present in all eukaryotes
- All cells do not have Endoplasmic reticulum. It is generally absent in egg and embryonic cells
Endoplasmic Reticulum Structure
Components of endoplasmic reticulum
Cisternae
- Formed by projection of nuclear membrane
- They bear ribosomes on the surface
- Contain ribophorin that bind the ribosomes
Vesicles
- They are oval or rounded, vacuole like element
- Many vesicles are free in the cytoplasm
Tubules
- They are tube like extensions
- Tubules are irregular and branched
- Free of ribosomes
Types of Endoplasmic Reticulum
I) Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
- Ribosomes binds with help of ribophorin protein
- Mainly composed of cisternae
- Abundantly occurs in cell which are engaged in protein synthesis and secretion
- Mass of RER in cyton of nueron is called missals granules
- g. Liver, pancreas and goblet cells
II) Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
- Ribosomes and ribophorins are absent
- Mainly composed of tubules
- Occurs especially in those cells which are almost inactive in protein synthesis
- It is well developed in cells that synthesis lipids
- Mass of SER in retinal cell is called myeloid bodies
Functions of Endoplasmic Reticulum
- It gives mechanical support so also called cytoskeleton of cell
- Intracellular exchange: Transport of materials in cytoplasm from one place to another through the ER
- Provides site for protein synthesis, because rough ER has ribosome’s
- Lipids synthesized by smooth ER
- Detoxification of drugs

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months ago[PPT] Human Reproduction Class 12 Notes
- Blog8 months ago
Contribution of Indian Phycologists (4 Famous Algologist)
- Blog8 months ago
PG TRB Botany Study Material PDF Free Download

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoCell The Unit of Life Complete Notes | Class 11 & NEET Free Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months ago[PPT] The living world Class 11 Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoPlasma Membrane Structure and Functions | Free Biology Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoJulus General Characteristics | Free Biology Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoClassification of Algae By Fritsch (11 Classes of Algae)













