Blog
Hydra Diagram, Structure and Reproduction | Free Biology Notes
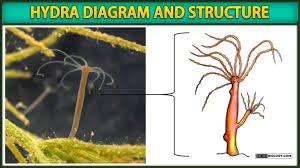
In this article we will discuss about hydra diagram, structure and reproduction
Structure of Hydra
Hydra is a type of invertebrate with the following structures:
Hydra Reproduction
Hydras, have the remarkable ability to reproduce in multiple ways. Let’s explore the different types of reproduction in hydra:
1. Asexual Reproduction:
Asexual reproduction is a common method employed by hydras to increase their population rapidly. In this process, a single hydra can generate offspring without the involvement of a mate. Here are two distinct mechanisms of asexual reproduction in hydras:
Budding: Budding is a prevalent form of asexual reproduction in which a small bud emerges from the body of the parent hydra. This bud gradually develops into a genetically identical clone of the parent, eventually detaching and becoming an independent hydra. Budding allows for rapid colony expansion and the colonization of new habitats.
Regeneration: Hydras possess an extraordinary ability to regenerate lost body parts. If a hydra is injured or fragments, each fragment has the potential to regenerate and form a complete hydra. Through this process, the hydra can repair damaged tissues and restore its complete form.
2. Sexual Reproduction:
Hydras also engage in sexual reproduction, which involves the fusion of specialized reproductive cells from two parent hydras. Sexual reproduction introduces genetic diversity into the population and allows for the creation of offspring with unique combinations of traits. Here’s an overview of sexual reproduction in hydras:
- Hermaphroditism: Hydras are hermaphroditic, meaning that each individual possesses both male and female reproductive organs. Within the same hydra, the testes produce sperm, while the ovaries produce eggs. This unique trait enables hydras to function as both male and female during sexual reproduction.
- Gamete Release: When the time is right for reproduction, the hydra releases sperm and eggs into the surrounding water. These reproductive cells are then able to meet and fuse, leading to the formation of a fertilized egg, or zygote.
- Embryo Development: The fertilized egg undergoes development and forms an embryo. The embryo may remain attached to the parent hydra or be released into the water, depending on the species. Eventually, the embryo develops into a fully-formed hydra.

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months ago[PPT] Human Reproduction Class 12 Notes
- Blog8 months ago
Contribution of Indian Phycologists (4 Famous Algologist)
- Blog8 months ago
PG TRB Botany Study Material PDF Free Download

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoCell The Unit of Life Complete Notes | Class 11 & NEET Free Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months ago[PPT] The living world Class 11 Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoPlasma Membrane Structure and Functions | Free Biology Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoJulus General Characteristics | Free Biology Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoClassification of Algae By Fritsch (11 Classes of Algae)













