Blog
Nervous Tissue Characteristics
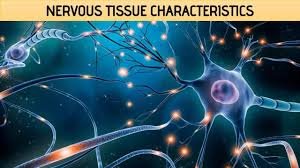
In this article we will discuss about the nervous tissue characteristics
Nervous Tissue Characteristics
- Nervous tissue is highly specialised to transmitting the stimulus very rapidly from one place to another within the body
- Nerve tissue is the main tissue of our nervous system
- Nervous tissue found in brain, spinal cord and nerves throughout body
- Nervous tissue consists of two cells: nerve cells (neuron) and neuroglia
- Nervous cells are basic cellular unit of nervous system
- Nerve cells live and function optimally for lifetime
- Neurons lose their ability to divide and cannot be replaced if destroyed
- Nerve cells vary in shape and size, all neurons contain three parts- cell body, dendrites and axon
- Cell body which contains the nucleus, cytoplasm and cell organelles
- Dendrite is a highly branched cytoplasmic extension, responsible for receiving impulses from outside & pass to the cyton
- Axons are long stem-like projections emerging out of the cell, it conducts nerve impulse away from cell body
- Neuroglia are non-conducting cells that protect and nurture as well as support cells of nervous tissue.
- Nervous tissue requires continuous and abundant supplies of oxygen and nutrients
- Nervous tissue transmits nerve impulses across body and coordinate, regulate, integrate body functions

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months ago[PPT] Human Reproduction Class 12 Notes
- Blog8 months ago
Contribution of Indian Phycologists (4 Famous Algologist)
- Blog8 months ago
PG TRB Botany Study Material PDF Free Download

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoCell The Unit of Life Complete Notes | Class 11 & NEET Free Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoPlasma Membrane Structure and Functions | Free Biology Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months ago[PPT] The living world Class 11 Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoJulus General Characteristics | Free Biology Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoClassification of Algae By Fritsch (11 Classes of Algae)