Blog
Platyhelminthes General Characteristics, Classification and Examples | Free Biology Notes
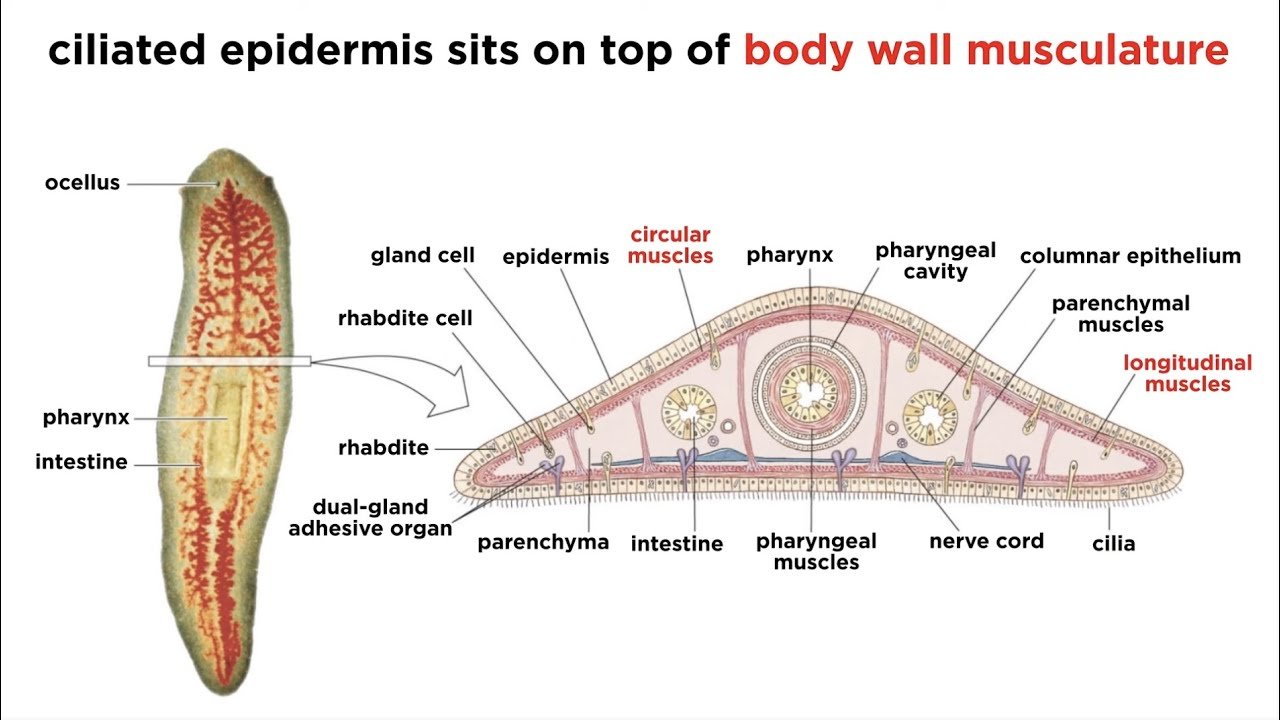
After reading this article you will learn about Platyhelminthes General Characteristics and classification.
Platyhelminthes General Characteristics
- Most are Parasitic on other animals and some are free living forms
- They have dorsoventrally flattened body hence are called flat worms
- Body is formed from three germinal layers
- Locomotory organs are absent in these animals but adhesive organs like suckers, hook are present in parasitic form
- On the body wall of parasitic animals a thick cuticle is present called tegument
- These thick cuticle protects the parasite from the digestive enzymes of the host
- Muscles in the body wall are mesodermal
- Below the epidermis longitudinal, circular and oblique muscles are present
- Digestive system incomplete or absent
- Skeleton, respiration and circulatory system are absent
- They respire through body surface and anaerobic respiration is found in parasite
- Nervous system is ladder like, consist of a nerve ring and longitudinal nerve cords
- Excretion occurs through specialized cells called flame cells or solenocytes
- Some members possess high regeneration capacity
- Sense organ are better developed in free living forms (Cephalization)
- Asexual reproduction occurs by fragmentation in many freshwater flatworms
- In sexual reproduction they are hermaphroditic meaning each individual produces eggs and sperm
- Fertilization is internal and cross fertilization is predominant
- Life cycle is indirect or complicated with one or many larvae
Classification of platyhelminthes
Class 1. Turbellaria
- Freeliving in both fresh and marine water
- Body is unsegmented & leaf like
- Cilia on body surface
- Suckers absent. Adhesive organs present
- E.g. Planaria, Bipalium
Class 2. Trematoda
- Endoparasites or ectoparasites
- Body is unsegmented & leaf like
- Cuticle present and no cilia
- Sucker and some times hooks present
- E.g. Liver Fluke, Schistostomata
Class 3. Cestoda
- Endoparasites in alimentary canal of vertebrates
- Body is segmented & ribbon like
- Cuticle present and no cilia
- Sucker and hooks present
- E.g. Tapeworm, Echinococcus

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months ago[PPT] Human Reproduction Class 12 Notes
- Blog8 months ago
Contribution of Indian Phycologists (4 Famous Algologist)
- Blog8 months ago
PG TRB Botany Study Material PDF Free Download

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoCell The Unit of Life Complete Notes | Class 11 & NEET Free Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months ago[PPT] The living world Class 11 Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoPlasma Membrane Structure and Functions | Free Biology Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoJulus General Characteristics | Free Biology Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoClassification of Algae By Fritsch (11 Classes of Algae)













