Blog
Difference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell
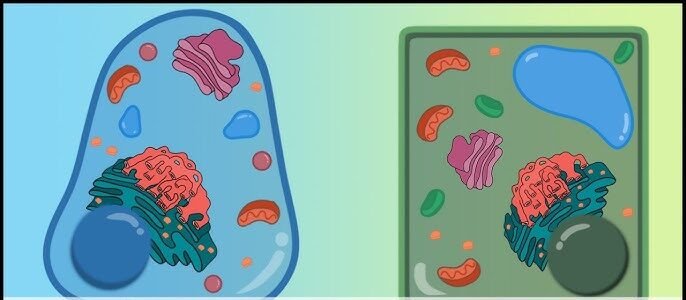
In this article we will discuss about difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell
Difference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell
1. Cell Size: Prokaryotic cells are generally smaller (0.1 to 5 micrometers), while eukaryotic cells are larger (10 to 100 micrometers).
2. Nucleus: Prokaryotic cells lack a defined nucleus. Their genetic material is present in the form of a single circular DNA molecule located in the nucleoid region. Eukaryotic cells have a well-defined nucleus that has multiple linear DNA molecules organized into chromosomes.
3. Membrane Bound Organelles: Prokaryotic cells lack membrane bound organelles, such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes. Eukaryotic cells possess these membrane bound organelles.
4. Ribosomes: Prokaryotic cells have smaller ribosomes (70S) compared to eukaryotic cells (80S), which are larger and more complex.
5. DNA Replication: Prokaryotic cells have a single point of origin for DNA replication, while eukaryotic cells have multiple origins of replication.
6. Cytoskeleton: Prokaryotic cells lack a cytoskeleton, whereas eukaryotic cells have a cytoskeleton composed of microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments that provide structural support and facilitate cell movement.
7. Cell Division: Prokaryotic cells divide by binary fission, a process where the cell duplicates its DNA and divides into two identical daughter cells. Eukaryotic cells undergo mitosis, followed by cytokinesis, resulting in the formation of two genetically identical daughter cells.
8. Complexity: Eukaryotic cells are generally more structurally and functionally complex than prokaryotic cells due to the presence of membrane bound organelles and a larger genome.
9. Reproduction: Prokaryotic cells reproduce asexually, while eukaryotic cells can reproduce both sexually and asexually.
10. Evolution: Prokaryotic cells represent the earliest forms of life on Earth and have been present for billions of years. Eukaryotic cells, on the other hand, evolved from prokaryotic ancestors through a process known as endosymbiosis.
Summary: Difference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell
- Prokaryotic cells are smaller and lack a defined nucleus, while eukaryotic cells are larger and have a well-defined nucleus.
- Prokaryotic cells lack membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells possess them.
- Prokaryotic cells have smaller ribosomes, while eukaryotic cells have larger and more complex ribosomes.
- Prokaryotic cells have a single point of origin for DNA replication, while eukaryotic cells have multiple origins of replication.
- Prokaryotic cells lack a well-developed cytoskeleton, while eukaryotic cells have a dynamic cytoskeleton.
- Prokaryotic cells divide by binary fission, while eukaryotic cells undergo mitosis and cytokinesis.
- Eukaryotic cells are generally more structurally and functionally complex than prokaryotic cells.
- Prokaryotic cells reproduce asexually, while eukaryotic cells can reproduce both sexually and asexually.
- Prokaryotic cells represent the earliest forms of life, while eukaryotic cells evolved from prokaryotic ancestors.

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months ago[PPT] Human Reproduction Class 12 Notes
- Blog8 months ago
Contribution of Indian Phycologists (4 Famous Algologist)
- Blog8 months ago
PG TRB Botany Study Material PDF Free Download

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoCell The Unit of Life Complete Notes | Class 11 & NEET Free Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months ago[PPT] The living world Class 11 Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoPlasma Membrane Structure and Functions | Free Biology Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoJulus General Characteristics | Free Biology Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoClassification of Algae By Fritsch (11 Classes of Algae)













