Blog
Vertebrata General Characteristics, Classification and Examples | Free Biology Notes
After reading this article you will learn about Vertebrata General Characteristics, Classification and Examples
Vertebrata General Characteristics
- Presence of brain box and vertebral column
- Notochord initially is embryonic, replaced by vertebral column in adult
- The circulatory system is closed with ventral chambered heart
- The blood plasma contains RBC and WBC
- Gill slits are limited in number (usually 5 pairs)
- Two pairs of appendages present
- Nerve cord is differentiates into brain and spinal cord
Classification of Vertebrata
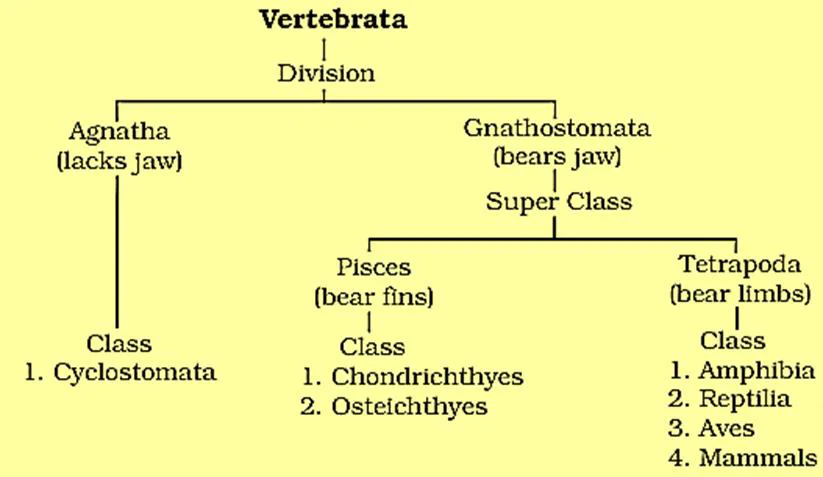
Subphylum vertebrata is divided into 2 divisions such as, Agnatha, the division which lacks jaw and Gnathostomata, the division which bears jaw.
Division 1. Agnatha
- Most of the members of this class are marine
- These fishes are ectoparasite as well as scavenger
- They have elongated body with 6-15 pairs of gills slits for respiration
- They have a sucking and circular mouth without jaws
- Scales and paired fins absent
- Notochord and vertebral column both are present. bones are absent
- Circulation is closed type, 2 chambered heart.
- Animals unisexual, fertilization external and larval stage is absent
- E.g. Petromyzon, Myxine etc.
Division 2. Gnathostomata
- Two well formed jaws encircle the mouth aperture in all members of this group.
- Paired and in some cases jointed appendages are present in Gnathostomata.
- Calcified, bony skull and vertebra are characteristic features of Gnathostomata.
- Divided into 2 super classes:- Pisces and Tetrapoda
Superclass 1. Pisces
- All aquatic and cold blooded fishes
- Body is long, spindle shaped and streamlined, which is divided into head, trunk and tail
- Body is covered by dermal scales, denticles or bony plates
- Locomotion with the help of various fins
- Respiration by gills
- Heart is two chambered, having one auricle and one ventricle
- External and middle ears are absent
- Lateral line system is well developed. help to sense water current vibrations
- Fishes are unisexual. Fertilization is internal or external and Development is direct
- Oviparous, viviparous or ovoviviparous
- Super class Pisces classified into two classes:- Chondrichthyes and Osteichthyes
Superclass 2. Tetrapoda
- Tetra-four, podos-feet
- Primarily terrestrial, some are secondarily aquatic in.
- Two pairs of pentadactyl limbs.
- Body covered by an exoskeleton of epidermal hair, feathers or scales.
- Lungs are main respiratory organs. Amphibian may respire by gills, skin or lungs.
- 3 or 4 chambered heart present.
- They are divided into 4 classes: Amphibia, Reptilia, Aves and Mammalia

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months ago[PPT] Human Reproduction Class 12 Notes
- Blog8 months ago
Contribution of Indian Phycologists (4 Famous Algologist)
- Blog8 months ago
PG TRB Botany Study Material PDF Free Download

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoCell The Unit of Life Complete Notes | Class 11 & NEET Free Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months ago[PPT] The living world Class 11 Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoPlasma Membrane Structure and Functions | Free Biology Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoJulus General Characteristics | Free Biology Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoClassification of Algae By Fritsch (11 Classes of Algae)













