Blog
Xylem – Definition, Types and Function | Free Biology Notes
This article we will discuss about Xylem – Definition, elements of xylem, types of xylem and functions of xylem
Xylem – Definition
- The term xylem was introduced by nageli (1858)
- Xylem is conducting tissue which conducts water and mineral nutrients upwards from the root to the leaves
- Xylem besides conduction also provide mechanical strength
- They are composed of four different types of cells
- The elements of xylem are xylem tracheids, xylem vessels, xylem fibres and xylem parenchyma
Elements of xylem
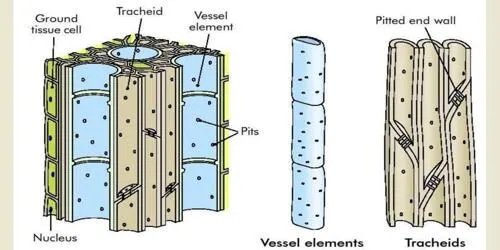
i) Tracheids
- Tracheids are dead and lignified cells
- Tracheids are elongated cell, thick walls with tapering end
- They are placed one above other and all separated by cross walls which bear bordered pits
- The deposition of lignin on cell wall is responsible for formation of different types of thickenings
- Types of thickening in tracheids are annular, spiral, scalariform, reticulate and border pitted
- Tracheids are found in pteridophytes, gymnosperms and xylem of dicotyledons
- Function: Conduct water, dissolved salts and also give mechanical support
ii) Vessels
- Vessels are dead and lignified cells
- Vessels are short cells, pipe like structure and thick walled with wide lumen
- Usually they have simple pits
- The deposition of lignin on cell wall is responsible for formation of different types of thickenings
- Types of thickening in vessels are annular, spiral, reticulate and pitted thickening
- The end walls of vessel elements are called perforation plates
- The perforation may be simple or multiple
- Function: Conduct water, dissolved salts and also give mechanical support
iii) Xylem fibres
- Xylem fibres are dead and lignified cells
- Fibres are long, thick walled and tapering ends
- Lumen is highly reduced
- They are generally not fount in gymnosperm wood
- Function: They give support to vessels and tracheids
iv) Xylem parenchyma
- Xylem parenchyma are living and thin walled cells
- Cell walls are made up of cellulose
- Function: Store food materials and radial conduction of water
Types of xylem
Basis of size and time of development
I) Protoxylem
- First formed xylem
- Consists of smaller elements
- Contain large amount of parenchyma
- Developed directly from procambium
II) Metaxylem
- Later formed xylem
- Consists of larger sized elements
- Contain less amount of parenchyma
- Differentiated part of the protoxylem
Based on position of primary xylem
I) Endarch
- Protoxylem elements are situated closer to centre of axis
- Metaxylem develops periphery
- Centrifugal development
- Feature of stems
II) Exarch
- Protoxylem elements are directed away from centre of axis
- Metaxylem elements develop towards centre of axis
- Centripetal development
- Feature of root
III) Mesarch
- Protoxylem elements are in centre surrounded by metaxylem elements
- Feature of ferns
Function of xylem
- The main function of xylem is to carry water and mineral salts upward from the root to different parts of shoots.
- Since walls of tracheids, vessels and sclerenchyma of xylem are lignified, they give mechanical strength to the plant body

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months ago[PPT] Human Reproduction Class 12 Notes
- Blog8 months ago
Contribution of Indian Phycologists (4 Famous Algologist)
- Blog8 months ago
PG TRB Botany Study Material PDF Free Download

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoPlasma Membrane Structure and Functions | Free Biology Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoCell The Unit of Life Complete Notes | Class 11 & NEET Free Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months ago[PPT] The living world Class 11 Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoJulus General Characteristics | Free Biology Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoClassification of Algae By Fritsch (11 Classes of Algae)