Blog
Evidence for Evolution Short Notes | Evolution Class 12 Notes
In this article we will discuss about Evidence for Evolution:- 1. Morphological and Anatomical evidence, 2. Embryological evidence, 3. Paleontological evidence and 4. Molecular evidence
- Evolution of life forms has taken place on earth have many proofs
- Morphological and Anatomical evidence
- Embryological evidence
- Paleontological evidence
- Molecular evidence
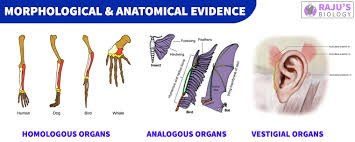
1. MORPHOLOGICAL & ANATOMICAL EVIDENCE

i) HOMOLOGOUS ORGANS:
- This organs have same structure and origin but may perform different functions
- Forelimbs of whales, humans, birds & dogs
- Axillary bud of bougainvillea and passiflora
ii) ANALOGOUS ORGANS:
- This Organs have different structure and origin but perform the same function
- Wings of insects, bats and birds
- Stem of Opuntia and Leaves
iii) VESTIGIAL ORGANS:
- Some organs do not perform any function in the body but functional in related animals
- This organs may functional in their ancestors
- E.g. Nictitating membrane, Wisdom tooth and Auricular muscles
iv) ATAVISM OR REVERSION:
- Reappearance of an ancestral trait in an organism after several generations of absence
- E.g. Tail in new born, Functional Auricular muscles and Werewolf syndrome
v) CONNECTING LINK:
- The living organisms having the characters of two different group of organisms
- They indicate evolution of one group of organisms from another group
- Protopterus:
- Connecting link between the fishes and amphibian
- Fish: Paired fins, appearance and gills
- Amphibian: Lungs, Heart and Internal nostrils
- Ornithorhynchus:
- Connecting link between the mammalia and amphibian
- Amphibian: Lays egg
- Mammalia: Mammary gland
2. EMBRYOLOGICAL EVIDENCES
i) Embryo Development Stages Similar in Triploblastic Organisms
Zygote > Blastula > Gastrula > 3 germ layers
ii) Early embryonic development in vertebrates
Fishes, Amphibians , reptiles, birds and mammals have similar embryonic development
Early embryos have tails, Gill slits, eyes and ear buds
iii) Recaptitulation theory
Proposed by Von Baer (Father of embryology)
In embryonic stages general characters appear firstly and specialized characters appear later
General characters – Brain, Spinal cord and axial skeleton
Specialized characters – Feathers in Birds and Hairs in mammals
3. PALAEONTOLOGICAL EVIDENCES
- Study of fossils is called paleontology
- Fossils are remains of organisms which existed long time ago
- They appear either as skeletal remains, footprints, molds or intact structures
- Age of fossils is determined by carbon dating
- By studying fossils, we are able to establish similarities between organism in present to its ancestor
- Fossils are very important to prove theory of evolution and common ancestry
i) MISSING LINKS:
- Connecting links which are not found in present times are called missing links
- Hypothetical fossil form intermediate between two living forms
- E.g. Archaeopteryx
- Missing link between reptiles and birds
- Reptile: Tail and tooth
- Avian: Feathers, Beak & wings
ii) STRATA OF SOIL:
- Soil is made up of distinct layers
- Top layers newer and bottom being older
- Fossils found in different strata at same site
- These unique features can be used to compare the ages of fossils
4. MOLECULAR EVIDENCE
- Scientists compare the similarity of genes (DNA) & proteins to study the relatedness of living species
- Using the rate of DNA mutation to estimate when species changed
- Composition and structure of protoplasm, enzymes, hormones and blood in chordates is almost same
- It shows that organisms have common ancestors

 Entertainment1 month ago
Entertainment1 month agoIbomma Bappam: Redefines Telugu Streaming Trend

 Blog1 month ago
Blog1 month ago[PPT] The living world Class 11 Notes

 Blog1 month ago
Blog1 month ago[PPT] Human Reproduction Class 12 Notes
- Blog1 month ago
Class 12 Biology Notes Chapter wise PPT

 Blog1 month ago
Blog1 month agoIosmirror.cc Apk: Enables Smart Screen Sharing
- Blog1 month ago
PG TRB Botany Study Material PDF Free Download
- Blog1 month ago
Class 11 Biology Notes Chapter wise PPT

 Blog1 month ago
Blog1 month agoDownload NEET Biology Study Materials in Tamil