Blog
Difference Between Gram Positive and Gram Negative Bacteria
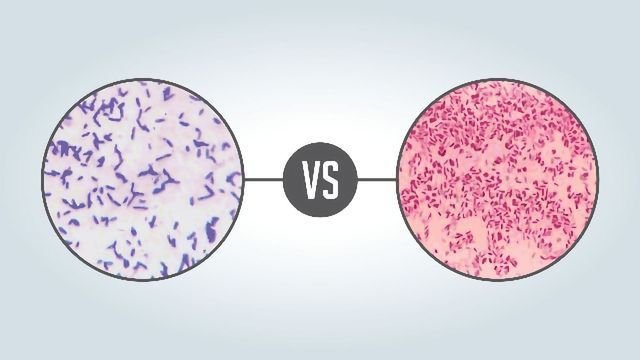
In this article we will discuss about difference between gram positive and gram negative bacteria
Difference Between Gram Positive and Gram Negative Bacteria
1. Cell Wall Structure: Gram positive bacteria have a thick peptidoglycan layer in their cell wall, which retains the crystal violet stain during the staining process. In contrast, gram-negative bacteria have a thin peptidoglycan layer and an additional outer membrane composed of lipopolysaccharides (LPS) that makes them impermeable to the crystal violet stain.
2. Staining: Gram positive bacteria retain purple color of crystal violet stain, while gram-negative bacteria do not and instead take up the counterstain safranin, which gives them a pink or red color.
3. Lipopolysaccharides (LPS): Gram-negative bacteria possess LPS in their outer membrane, which consists of lipid A, core polysaccharide, and O-specific polysaccharide. LPS acts as an endotoxin and contributes to the virulence of gram-negative bacteria.
4. Porins: Gram-negative bacteria have porin proteins in their outer membrane, which form channels for the transport of molecules across the membrane. Gram-positive bacteria lack an outer membrane and do not possess porins.
5. Antibiotic Susceptibility: Gram-positive bacteria are generally more susceptible to antibiotics than gram-negative bacteria due to the differences in their cell wall structure. The thick peptidoglycan layer in gram-positive bacteria makes them more susceptible to cell wall targeting antibiotics, while the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria acts as a barrier against many antibiotics.
6. Toxins: Gram-negative bacteria produce endotoxins, which are released upon cell lysis, while gram-positive bacteria produce exotoxins, which are secreted by the bacteria and can cause damage to host cells.
7. Sensitivity to Lysozyme: Lysozyme, an enzyme found in tears, saliva, and other body fluids, can break down the peptidoglycan layer in bacterial cell walls. Gram-positive bacteria are more sensitive to lysozyme due to their thick peptidoglycan layer, while gram-negative bacteria are more resistant to its action.
8. Resistance to Drying: Gram-positive bacteria have a higher resistance to drying compared to gram-negative bacteria due to the presence of a thick peptidoglycan layer that helps retain water.
9. Outer Membrane Permeability: Gram-negative bacteria have a higher outer membrane permeability than gram-positive bacteria due to the presence of porins and other transport proteins. This allows gram-negative bacteria to take up a wider range of nutrients and molecules from their environment.
10. Pathogenicity: Both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria can be pathogenic, but gram-negative bacteria are generally considered more virulent. The presence of endotoxins in gram-negative bacteria and the ability to evade host immune responses through various mechanisms contribute to their pathogenicity.
Summary : Difference between gram positive and gram negative bacteria
- Gram-positive bacteria have a thick peptidoglycan layer in their cell wall, while gram-negative bacteria have a thin peptidoglycan layer and an outer membrane.
- Gram-positive bacteria retain the purple color of the crystal violet stain, while gram-negative bacteria take up the pink or red color of the counterstain.
- Gram-negative bacteria possess lipopolysaccharides (LPS) in their outer membrane, while gram-positive bacteria do not.
- Gram-negative bacteria have porins in their outer membrane, while gram-positive bacteria lack an outer membrane and porins.
- Gram-positive bacteria are generally more susceptible to antibiotics than gram-negative bacteria.
- Gram-negative bacteria produce endotoxins, while gram-positive bacteria produce exotoxins.
- Gram-positive bacteria are more sensitive to lysozyme, while gram-negative bacteria are more resistant.
- Gram-positive bacteria have higher resistance to drying than gram-negative bacteria.
- Gram-negative bacteria have higher outer membrane permeability than gram-positive bacteria.
- Gram-negative bacteria are generally considered more virulent than gram-positive bacteria.

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months ago[PPT] Human Reproduction Class 12 Notes
- Blog8 months ago
Contribution of Indian Phycologists (4 Famous Algologist)
- Blog8 months ago
PG TRB Botany Study Material PDF Free Download

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoCell The Unit of Life Complete Notes | Class 11 & NEET Free Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months ago[PPT] The living world Class 11 Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoPlasma Membrane Structure and Functions | Free Biology Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoJulus General Characteristics | Free Biology Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoClassification of Algae By Fritsch (11 Classes of Algae)













