Blog
Internal Structure of Monocot Stem Notes | Free Biology Notes
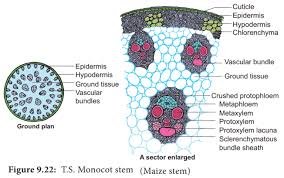
This article we will discuss about Internal Structure of Monocot Stem
The transverse section of a monocot stem reveals the following structures
Epidermis
- Epidermis is a outermost layer and made up of parenchymatous cells
- Cuticle is a protective layer, covers this layer
- Trichomes or hairs are lacking
- Epidermis has following functions
- Minimize the rate of transpiration
- Protects from mechanical injury
- Prevents the entry of harmful organisms
- Helps in the exchange of gases through stomata
Hypodermis
- This layer present just below the epidermis and multi-layered of sclerenchyma cells
- Hypodermis has following functions: helps in mechanical support
Cortex
- Its present below the hypodermis and made up of rounded cells of parenchyma cells
- There is no differentiation of general cortex, endodermis, pericycle, pith, and rays
- In some grasses, wheat etc. the central portion of ground tissue becomes hollow is called pith cavity
- Ground tissue has following functions: Storage of food
Vascular bundles
- Vascular bundles are irregularly scattered in the ground tissues is called atactostele
- These are conjoint, collateral, and closed vascular bundle
- Vascular bundles in the peripheral region are smaller in size and compactly arranged
- Vascular bundles in the central region are larger in size and widely placed
- Vascular bundles oval in shape and surrounded by a sheath of sclerenchymatous tissue is called bundle sheath
- Vascular bundle consists of xylem and phloem
- Ground tissue has following functions: conduction of water and food materials

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months ago[PPT] Human Reproduction Class 12 Notes
- Blog8 months ago
Contribution of Indian Phycologists (4 Famous Algologist)
- Blog8 months ago
PG TRB Botany Study Material PDF Free Download

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoCell The Unit of Life Complete Notes | Class 11 & NEET Free Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months ago[PPT] The living world Class 11 Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoPlasma Membrane Structure and Functions | Free Biology Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoJulus General Characteristics | Free Biology Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoClassification of Algae By Fritsch (11 Classes of Algae)














