Blog
Similarities Between Mitochondria and Chloroplast
In this article we will discuss about similarities between mitochondria and chloroplast
Similarities Between Mitochondria and Chloroplast
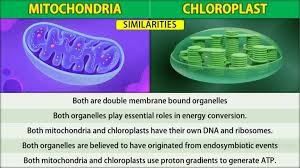
1. Organelle Structure: Both mitochondria and chloroplasts are double membrane bound organelles found in eukaryotic cells.
2. Energy Conversion: Both organelles play essential roles in energy conversion. Mitochondria are responsible for cellular respiration, which generates adenosine triphosphate (ATP) through the breakdown of glucose. Chloroplasts, on the other hand, are involved in photosynthesis, converting sunlight into chemical energy in the form of glucose.
3. Inner Membrane System: Both organelles possess internal membrane systems that increase their surface area for biochemical reactions. In mitochondria, these structures are called cristae, while in chloroplasts, they are known as thylakoids.
4. DNA and Ribosomes: Both mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own DNA and ribosomes. This indicates that they can partially produce their own proteins, suggesting an endosymbiotic origin.
5. Endosymbiotic Theory: Both organelles are believed to have originated from endosymbiotic events in the evolutionary past. Mitochondria are thought to have evolved from engulfed aerobic bacteria, while chloroplasts are believed to have originated from engulfed photosynthetic bacteria.
6. Replication: Both mitochondria and chloroplasts can replicate independently within a cell through a process similar to binary fission. This ability to divide is evidence of their separate evolutionary origins.
7. Genetic Material: Both organelles contain genetic material that is distinct from the cell’s nuclear DNA. This genetic material encodes for specific proteins required for their respective functions.
8. Energy Storage: Both mitochondria and chloroplasts can store energy in the form of chemical compounds. Mitochondria store energy in the form of ATP, while chloroplasts store energy in the form of glucose and other carbohydrates.
9. Membrane Transport: Both organelles have specialized transport proteins embedded in their membranes that facilitate the exchange of ions and metabolites with the surrounding cytoplasm.
10. Proton Gradient: Both mitochondria and chloroplasts use proton gradients to generate ATP. In mitochondria, protons are pumped across the inner mitochondrial membrane, while in chloroplasts, protons are pumped across the thylakoid membrane.

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months ago[PPT] Human Reproduction Class 12 Notes
- Blog8 months ago
Contribution of Indian Phycologists (4 Famous Algologist)
- Blog8 months ago
PG TRB Botany Study Material PDF Free Download

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoPlasma Membrane Structure and Functions | Free Biology Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoCell The Unit of Life Complete Notes | Class 11 & NEET Free Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months ago[PPT] The living world Class 11 Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoClassification of Algae By Fritsch (11 Classes of Algae)

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoJulus General Characteristics | Free Biology Notes