Blog
Similarities Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
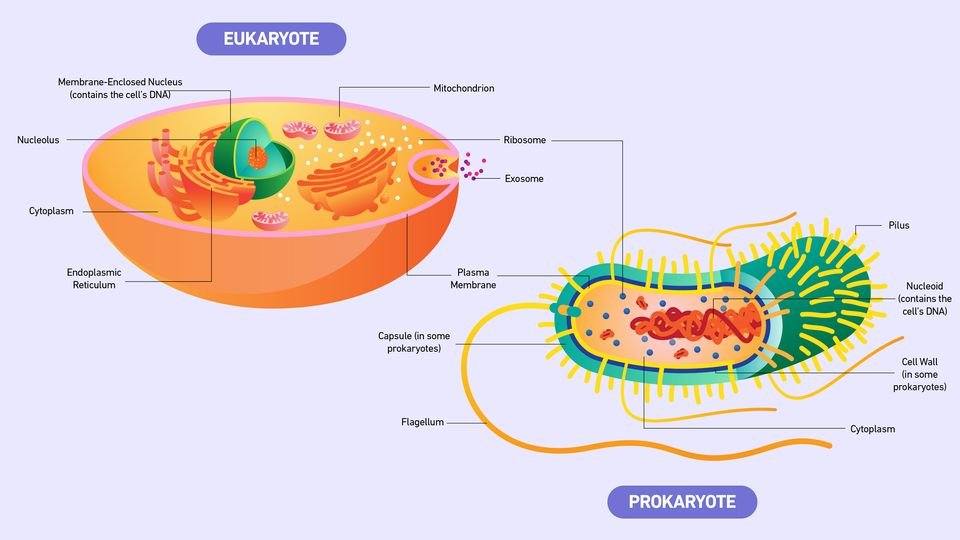
In this article we will discuss about similarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
Similarities Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
1. Plasma Membrane: Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have a plasma membrane that function is controlling the movement of substances into and out of the cell.
2. Genetic Material: Both types of cells contain genetic material in the form of DNA, which carries the hereditary information necessary for cell function and reproduction.
3. Transcription and Translation: Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells undergo transcription and translation, where DNA to RNA then it’s translated into proteins.
4. Ribosomes: Both cell types have ribosomes. They are responsible for protein synthesis in both types of cells.
5. Cytoplasm: Both cells have a cytoplasm, a gel-like substance that fills the cell and present various cellular components.
6. Metabolism: Both types of cells carry out metabolic processes such as glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation to generate energy in the form of ATP.
7. Cellular Respiration: Both cells can carry out cellular respiration to generate ATP using glucose or other organic molecules as a fuel source.
8. Metabolic Pathways: Many metabolic pathways, such as glycolysis and the Krebs cycle, are shared between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, indicating a common ancestry and evolutionary conservation.
Summary: Similarities Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
- Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have a plasma membrane, genetic material (DNA), undergo transcription and translation, and contain ribosomes.
- Both cell types have cytoplasm, carry out metabolic processes, and use various mechanisms for cell membrane transport.
- Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells can perform cellular respiration and replicate their DNA prior to cell division.
- Many metabolic pathways are shared between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, indicating a common ancestry and evolutionary conservation.

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months ago[PPT] Human Reproduction Class 12 Notes
- Blog8 months ago
Contribution of Indian Phycologists (4 Famous Algologist)
- Blog8 months ago
PG TRB Botany Study Material PDF Free Download

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoCell The Unit of Life Complete Notes | Class 11 & NEET Free Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months ago[PPT] The living world Class 11 Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoPlasma Membrane Structure and Functions | Free Biology Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoJulus General Characteristics | Free Biology Notes

 Blog8 months ago
Blog8 months agoClassification of Algae By Fritsch (11 Classes of Algae)













